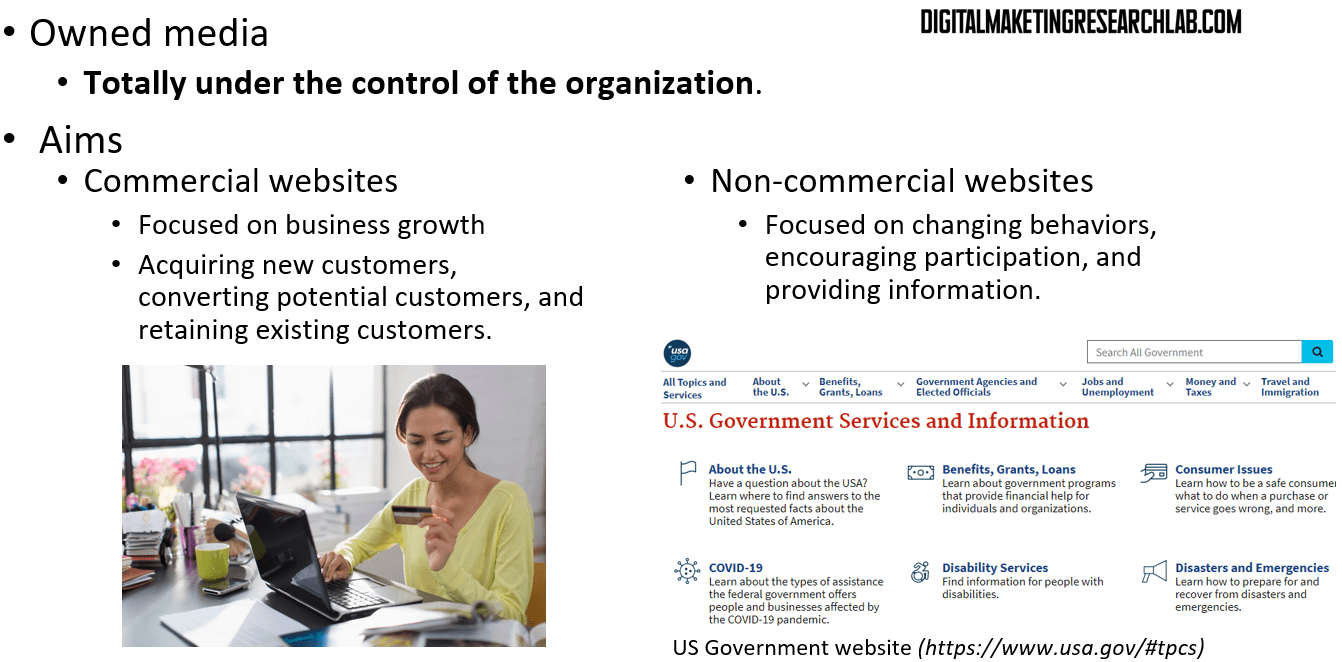
When it comes to digital marketing, an organization’s website is a powerful tool as an owned media channel under the full control of the organization. Since there are broadly two types of organizations—commercial organizations and non-commercial organizations—we can also identify two types of websites: commercial and non-commercial. Each type of website has distinct aims. Commercial websites are business-oriented, so their aims include acquiring new customers, converting potential customers, and retaining existing customers. Meanwhile, non-commercial websites (e.g., U.S. government websites) aim to change behaviors, encourage participation, and provide useful information.
Types of website
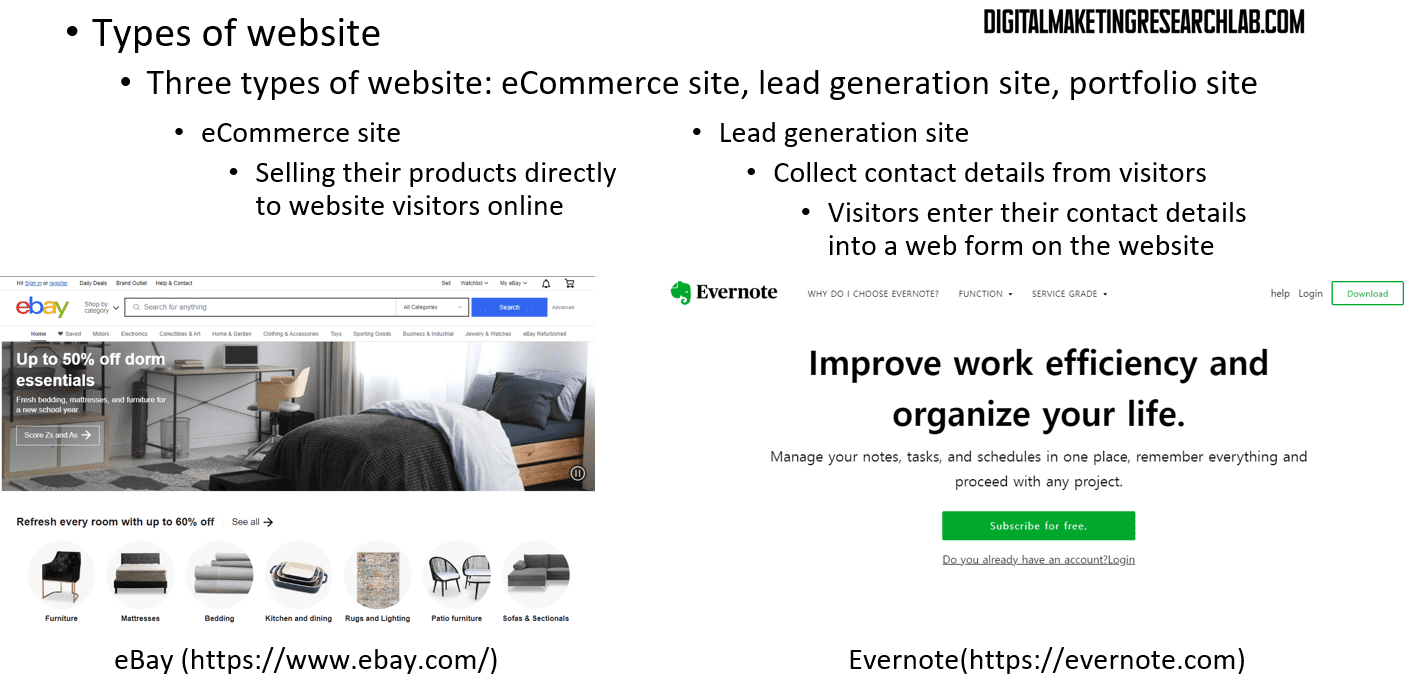
When we narrow the category of websites to commercial ones, there are mainly three types: eCommerce sites, lead-generation sites, and portfolio sites. eCommerce websites are designed to sell products directly to website visitors online. However, lead-generation sites do not sell products directly; instead, they collect visitors’ contact information by encouraging them to enter their details into a web form. These leads (or prospective customers) will eventually turn into real customers through targeted efforts by companies. Meanwhile, portfolio websites showcase products and services online, allowing visitors to learn about a company and its offerings by reading through the content.

All of these websites share common goals, such as increasing total and returning users, boosting users’ average time on site, and building positive brand affinity.

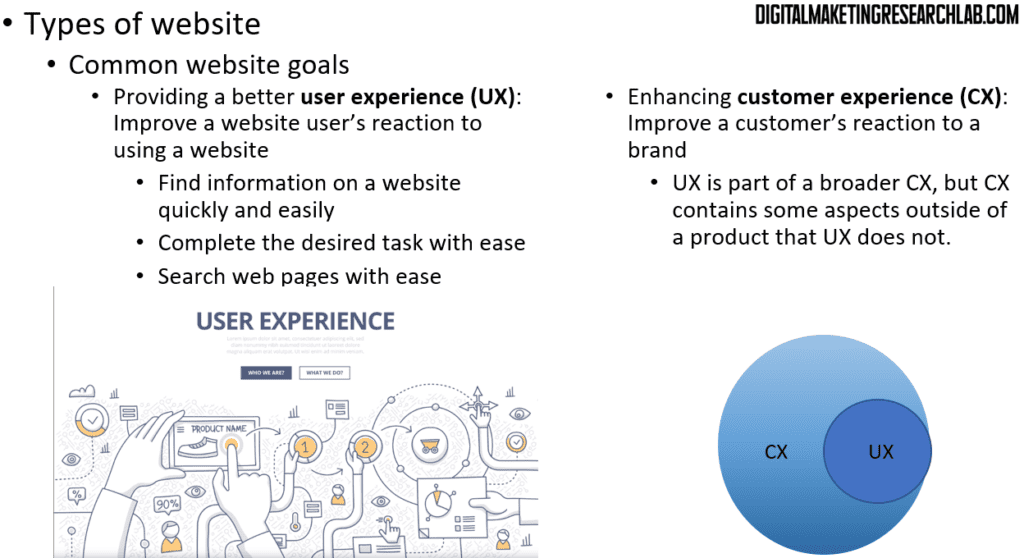
Beyond these goals, websites also aim to improve user experience (UX) and enhance customer experience (CX). UX refers to improving a website user’s reaction to using the site. In other words, users have better experiences when they can find information quickly and easily, complete desired tasks without difficulty, and navigate pages with ease. Meanwhile, CX refers to improving a customer’s reaction to a brand. Regarding the relationship between these two concepts, UX is part of a broader CX, but CX includes some aspects outside the product that UX does not.
To provide better user experience (UX) and customer experience (CX), a website should be free from friction. Friction refers to anything that makes it difficult for a visitor to complete an action, such as browsing the website. Potential friction points include confusing navigation, a slow checkout process, unclear benefits of converting, and a slow website.
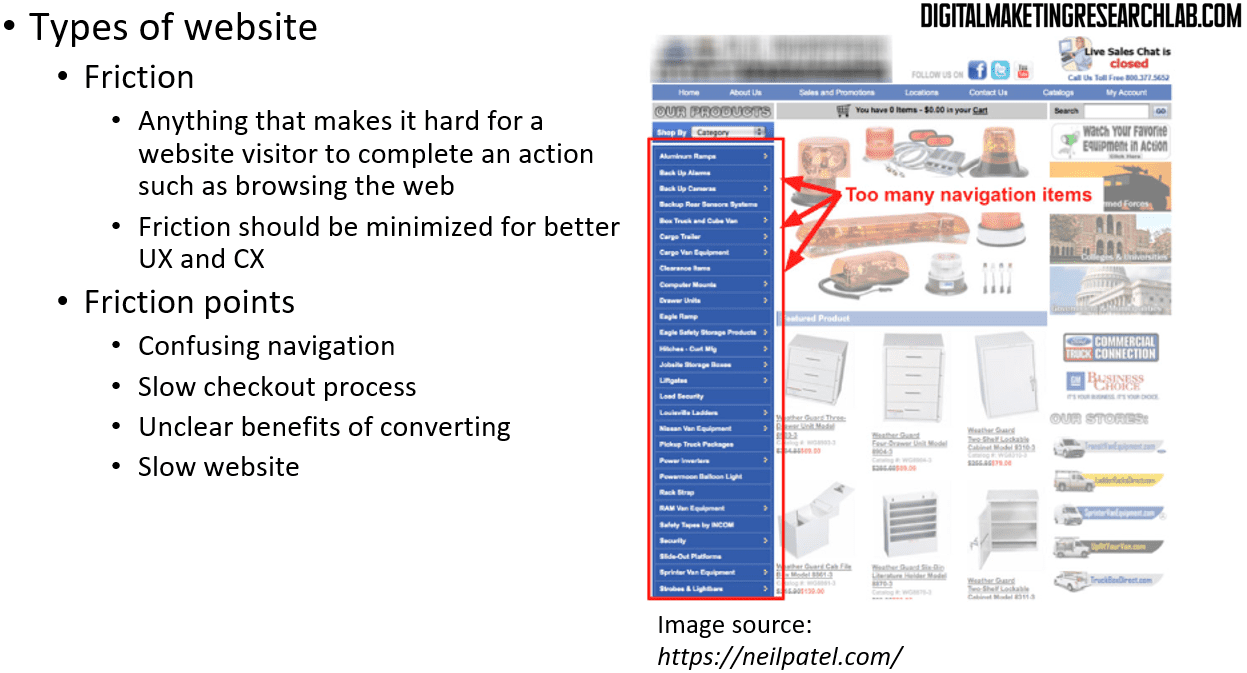
Meanwhile, eCommerce and lead-generation websites also have distinct goals. First, eCommerce sites aim to increase transactions and revenue and to improve eCommerce conversion rate, which is the percentage of people who visit the site and then make a purchase ( = sales / total visitors). Another goal is to increase average order value (AOV), which is the average amount someone spends when they buy ( = revenue / sales).
On the other hand, lead-generation sites aim to increase the number of qualified leads (i.e., the total number of high-quality leads) and to drive a higher lead-conversion rate (i.e., the percentage of website visitors who fill out a web form). They also strive to improve lead close rate, which is the percentage of qualified leads that the sales team successfully converts into customers.

Role of marketers in web design
Although web design is usually undertaken by web designers or developers, marketers should collaborate with them. Marketers should also take responsibility for branding, writing and editing content, and optimizing the website through search engine optimization (SEO). The role of marketers in web design further extends to preparing web data tracking and conducting data analysis. Well-known web analytics tools include Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics.

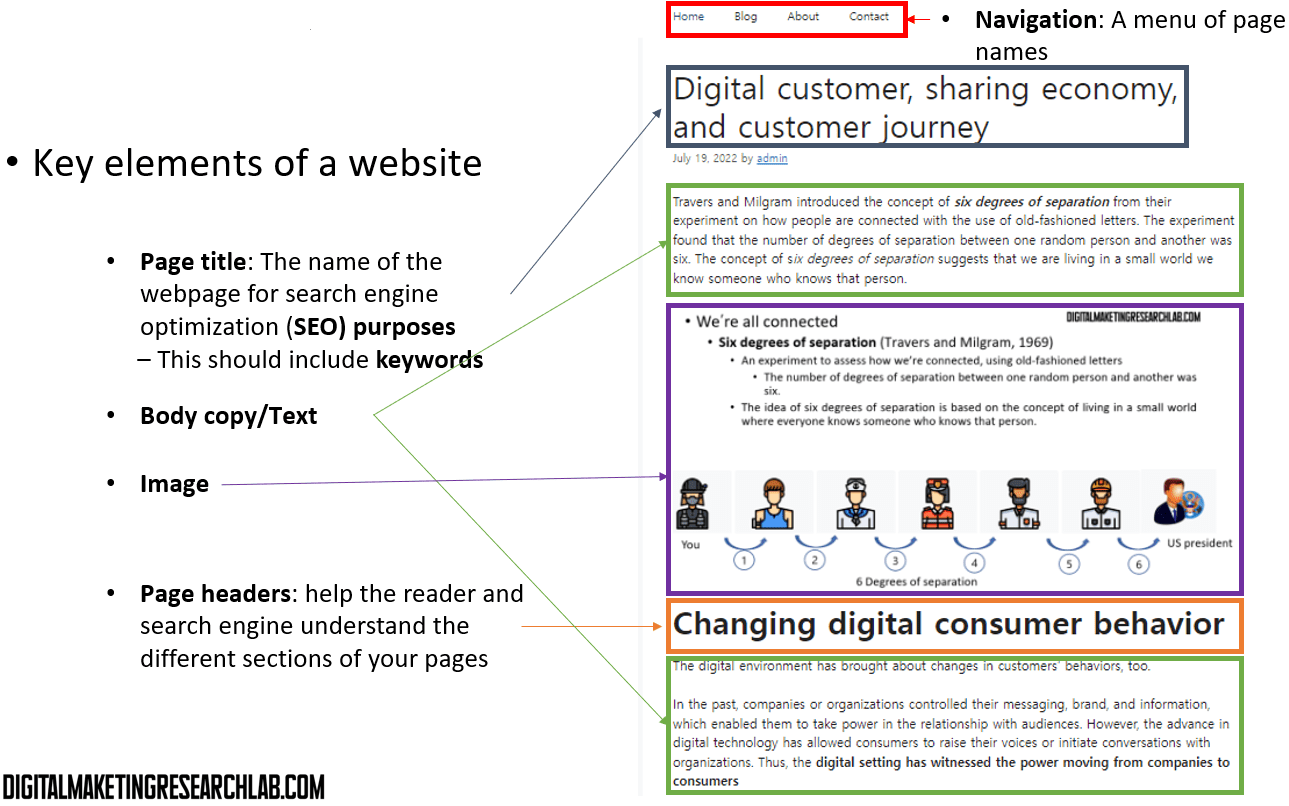
Key elements of a websiteWebpages include elements such as navigation, page titles, body copy, images, page headers, hero images, web forms, and call-to-action (CTA) buttons.
Typically, at the top of a webpage, you will find a navigation bar, which is a menu of page names. Below that appears a page title, which is the name of the webpage. A page title is one of the most crucial elements for search engine optimization (SEO) because it helps search engines rank the page higher on the search engine results page (SERP). Including keywords in a page title is a recommended SEO practice. Body copy refers to the written content on a webpage. Images are graphical elements that make a webpage more engaging and appealing to visitors. Page headers serve as headings that indicate transitions to different sections. Like page titles, page headers should include keywords for SEO purposes.
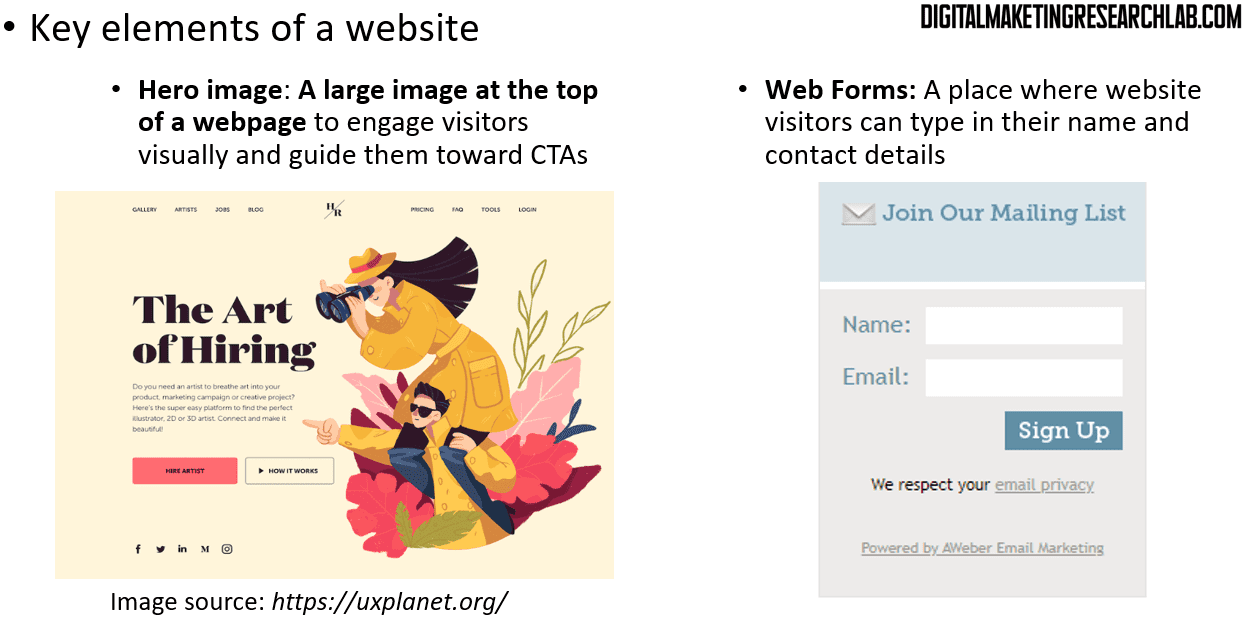
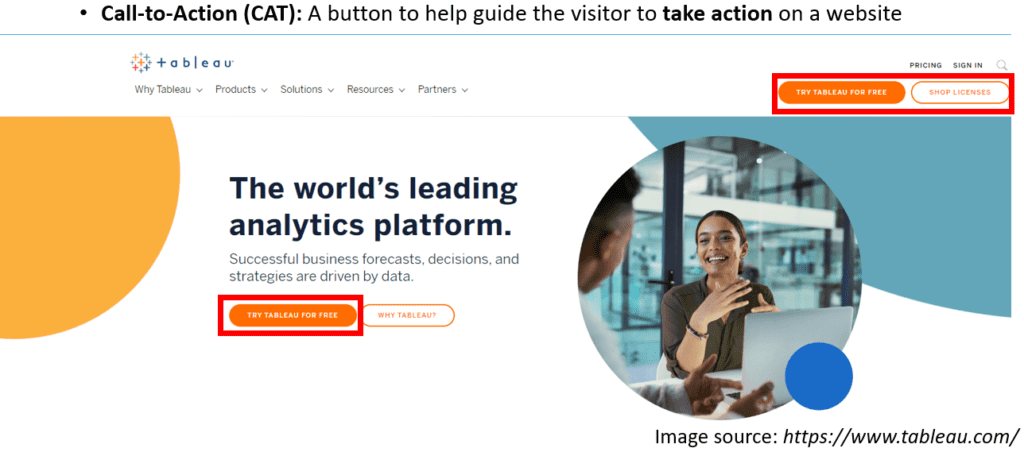
A hero image is the first large visual element visitors encounter and presents an overview of the website. It is often accompanied by a call-to-action (CTA). A web form is a space where visitors can enter their names and contact details in exchange for something valuable, such as e-books. A call-to-action (CTA) is a button designed to guide visitors to take specific actions on a website.
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.