Today we’re going to dive into the topic of search engine optimization, commonly referred to as SEO. SEO is the process of getting your website to show up in the free, organic search results on search engines like Google. This is different from paid advertising, where you have to pay to get your website displayed at the top of the search results.
SEO fundamentals
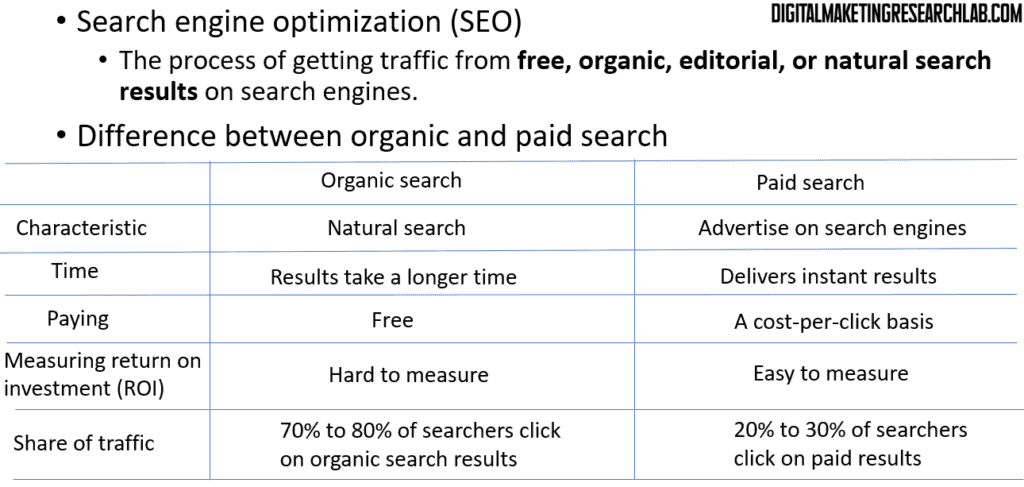
Let’s start with a definition of SEO. Search engine optimization is the process of getting traffic from free, organic, editorial, or natural search results on search engines. In other words, it’s about optimizing your website so that it ranks highly in the unpaid, natural search listings when people search for relevant keywords and phrases.
Now, there are some key differences between organic SEO and paid search advertising:
Organic search (SEO) delivers natural, unpaid search results. The main benefits are that it’s free and the traffic you get tends to be very high-quality, as these are people actively searching for what you offer. However, the downside is that it can take weeks or even months to start seeing results from your SEO efforts.
Paid search, on the other hand, allows you to instantly get your website to the top of the search results, but you have to keep paying for those ads to maintain that placement. Only 20-30% of searchers click on the paid ads, compared to 70-80% who click on the organic listings.
So in summary, organic SEO is free but slower, while paid search is fast but requires an ongoing advertising budget.
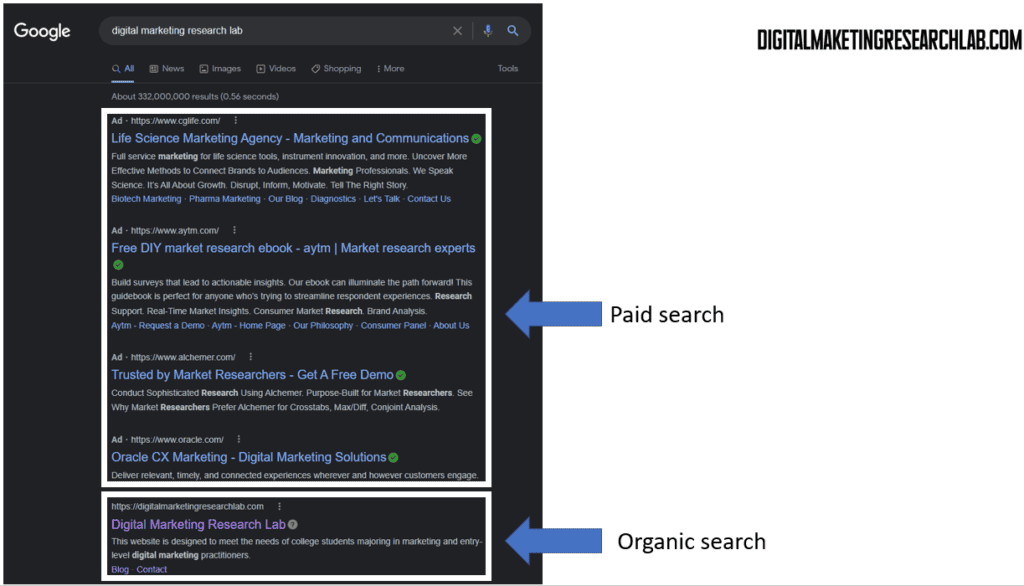
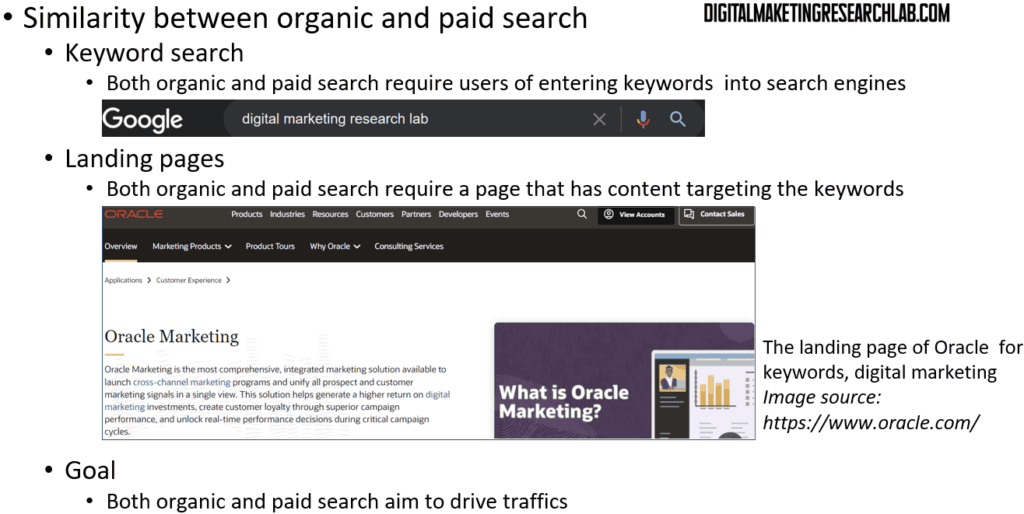
Despite the differences, organic SEO and paid search do share some key similarities:
Keyword research is critical for both. You need to identify the specific keywords and phrases that potential customers are using to search for businesses like yours. This informs the content and targeting for both your organic and paid campaigns.
Both also require you to have relevant landing pages on your website. For organic SEO, these need to be well-optimized pages that provide a good user experience. For paid search, you can either use those same pages or create specific landing pages just for your ads.
And ultimately, the goal of both organic and paid search is the same – to drive qualified traffic to your website that can convert into leads or sales.
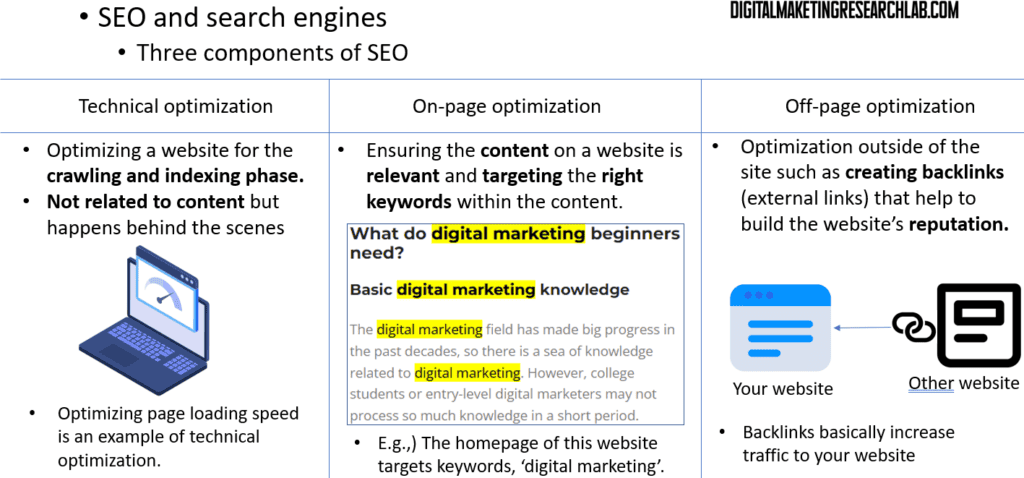
When it comes to the core of search engine optimization, there are three main pillars:
1. Technical optimization – This refers to all the behind-the-scenes work you do to make your website search engine-friendly. Things like site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability.
2. On-page optimization – This is about ensuring the actual content on your website is relevant and optimized around your target keywords. The goal is to make it as easy as possible for search engines to understand what your pages are about.
3. Off-page optimization – This involves building up your website’s reputation and authority through things like earning high-quality backlinks from other reputable sites.
Focusing on these three pillars is crucial for a comprehensive SEO strategy that can help you rank higher in the search results.
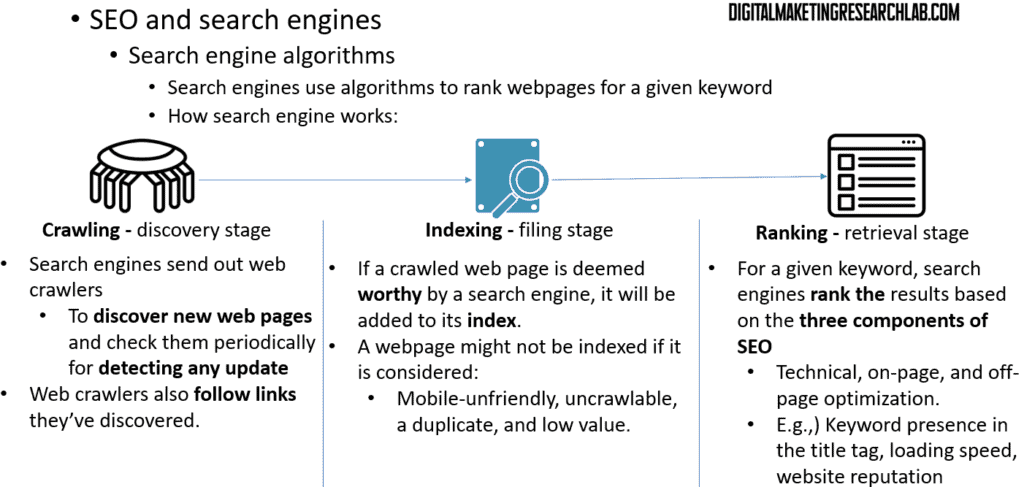
Let’s take a step back and look at how search engines actually work. There are three main phases:
1. Crawling – Search engine bots, often called “spiders” or “crawlers”, discover new web pages by following links. They continuously crawl the web to find updated content.
2. Indexing – Once a page is crawled, the search engine then has to decide whether to include it in its index. Pages that provide unique, valuable content are typically indexed.
3. Ranking – Finally, when someone performs a search, the search engine’s algorithm looks at over 200 different ranking factors to determine the order of the search results. This is where all your optimization efforts come into play.
Understanding this crawl-index-rank process is key to developing effective SEO strategies.
One of the most important Google ranking factors these days is something called RankBrain, which is the search engine’s machine learning algorithm.
To do well with RankBrain, there are a few best practices:
1) Target medium-tail keywords – These are keyword phrases that are more specific than broad, generic terms, but not so narrow that there’s very little search volume.
2) Optimize your page titles and meta descriptions for click-through rate. Make them enticing for users to click on in the search results.
3) Focus on creating content that satisfies the searcher’s intent and keeps people engaged on your pages. Metrics like dwell time and bounce rate are important signals to RankBrain.
By following these RankBrain optimization tips, you can give your SEO efforts a big boost.

There are three main types of keywords that people use when searching:
Informational keywords are broader queries where someone is just looking for general information, like “what is digital marketing?”. These make up the largest proportion of searches, but are also the hardest to convert into sales leads or customers.
Navigational keywords are when someone is trying to find a specific website or brand, like searching for “Digital Marketing Research Lab”. These happen at all stages of the buyer’s journey.
Transactional keywords indicate the person is ready to make a purchase, such as “hire digital marketers”. While these only make up a smaller percentage of overall searches, they’re typically the easiest to convert.
Understanding the intent behind these different keyword types is crucial for an effective SEO strategy.

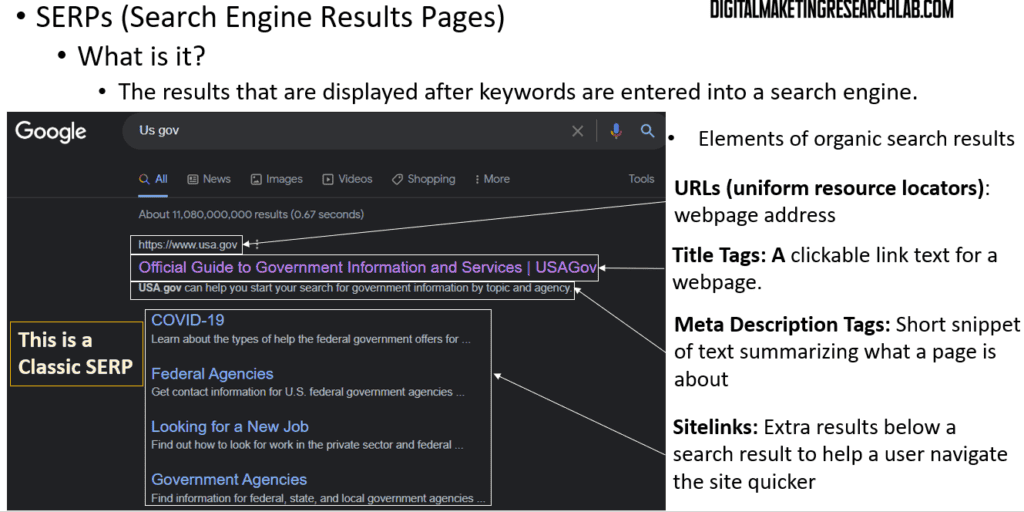
When someone performs a search on Google or another search engine, the results page they see is called the SERP, or Search Engine Results Page.
The key elements on a SERP include:
– The page URLs
– The clickable blue title tags
– The meta description snippets
– Any sitelinks that may appear
– And potentially rich snippets with additional information
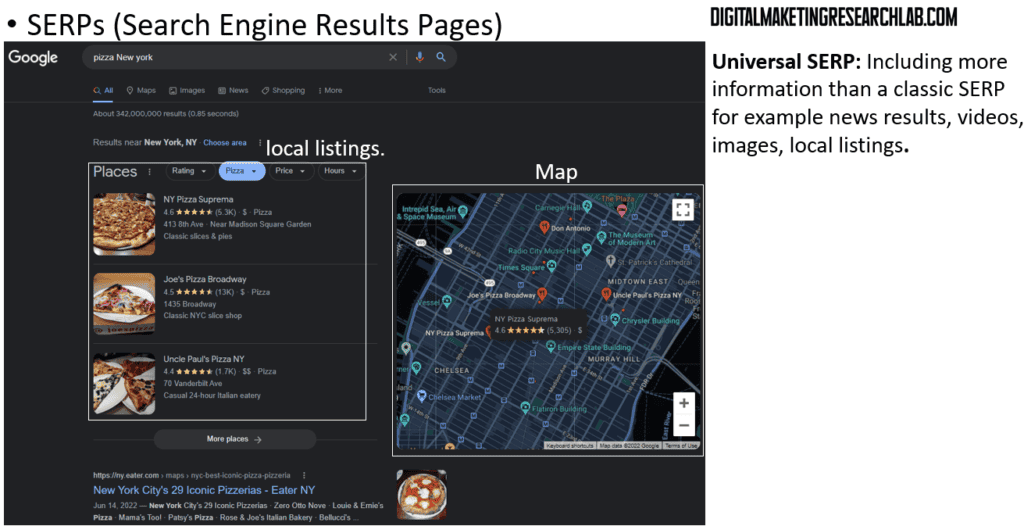
Search engines are constantly evolving their SERPs to provide the most useful and relevant information to searchers. This can include things like news results, images, videos, and local business listings.
Optimizing your pages to stand out effectively on the SERP is a critical SEO tactic.
Alingning SEO and business objectives
When setting SEO objectives for your business, it’s important to align them with your overall business goals and priorities.
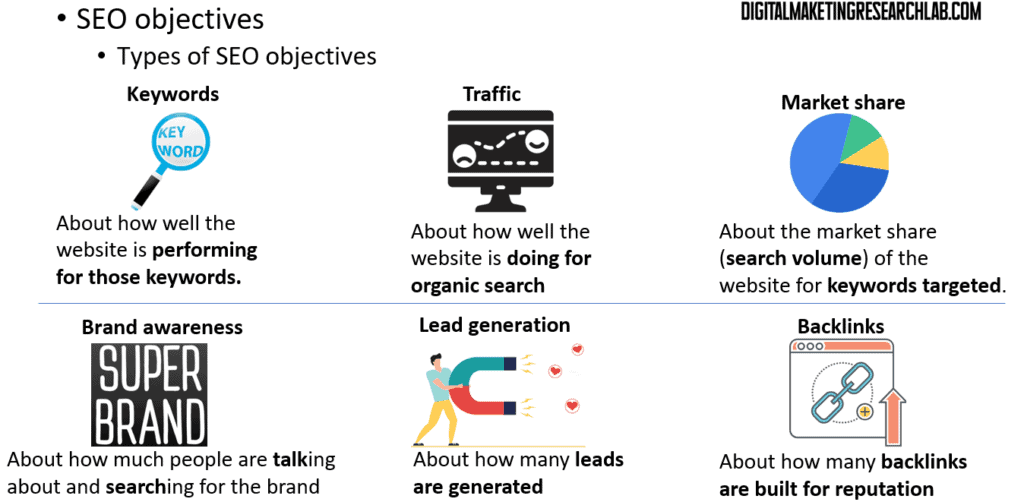
Some common SEO objectives include:
– Improving rankings and visibility for your target keywords
– Increasing organic website traffic
– Growing your market share for key search terms
– Building brand awareness through search
– Generating more qualified leads from organic search
– Earning high-quality backlinks to enhance your website’s authority
The specific objectives you set will depend on whether your business is more transactional, like an e-commerce site, or more informational, like a blog or content publisher.
But the key is to ensure your SEO efforts are directly contributing to the metrics that matter most for your company.
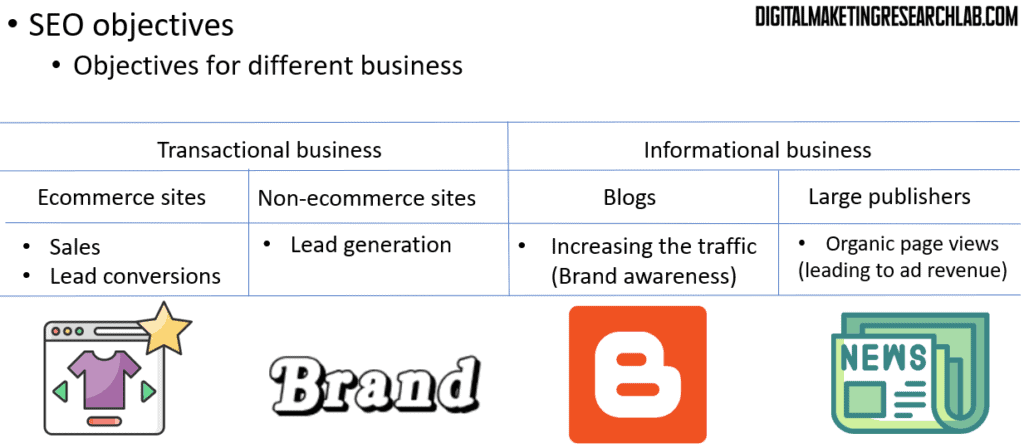
Keywords and building an SEO content plan
Then, let’s move onto keyword research. Keyword research is the process of discovering the keywords used by potential customers for a specific purpose, such as SEO. This allows you to effectively attract the customers who are looking for your products or services.
So, what are the main functions of keyword research? Firstly, through keyword research, you can identify the right visitors who have a high potential to convert into sales. Secondly, you can identify keywords with high search volume and disregard those with low search volume. Thirdly, you can identify content gaps between the content on your website and what customers are looking for. This allows you to create content that meets their needs. Lastly, you can differentiate between keywords that are highly competitive and those that are less competitive to rank for. This helps you effectively improve your search rankings.

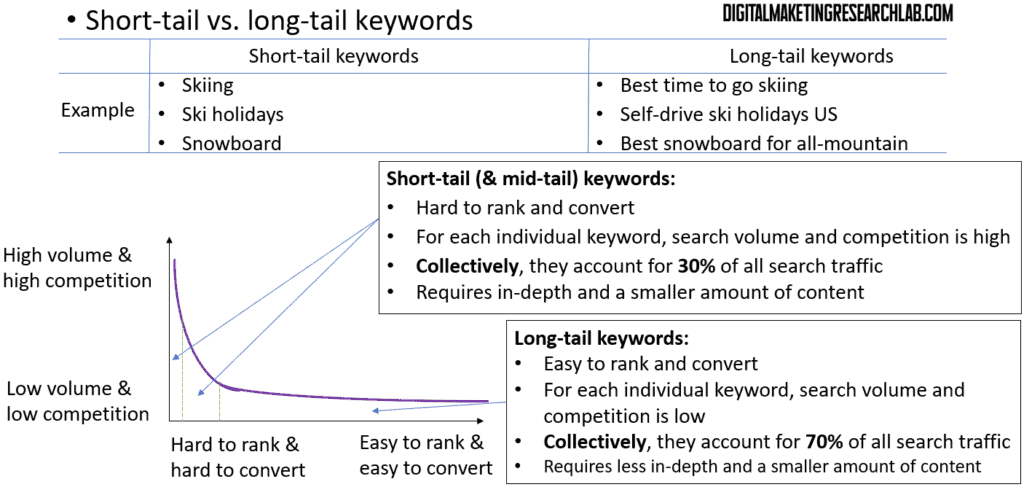
There’s an important distinction to understand between short-tail and long-tail keywords:
Short-tail keywords are very broad, generic terms, like “skiing” or “snowboards”. They tend to have high search volume, but are also highly competitive to rank for.
Long-tail keywords are more specific, multi-word phrases, such as “best time to go skiing” or “self-drive ski holidays in France”. While they have lower search volume individually, collectively long-tail keywords make up the majority of searches. And they’re generally easier to rank for compared to short-tail terms.
The key differences are that short-tail keywords are harder to rank and convert, while long-tail keywords are easier to rank and convert, despite having lower search volume per term.
Understanding this short-tail vs. long-tail dynamic is crucial when prioritizing your keyword focus and content creation.

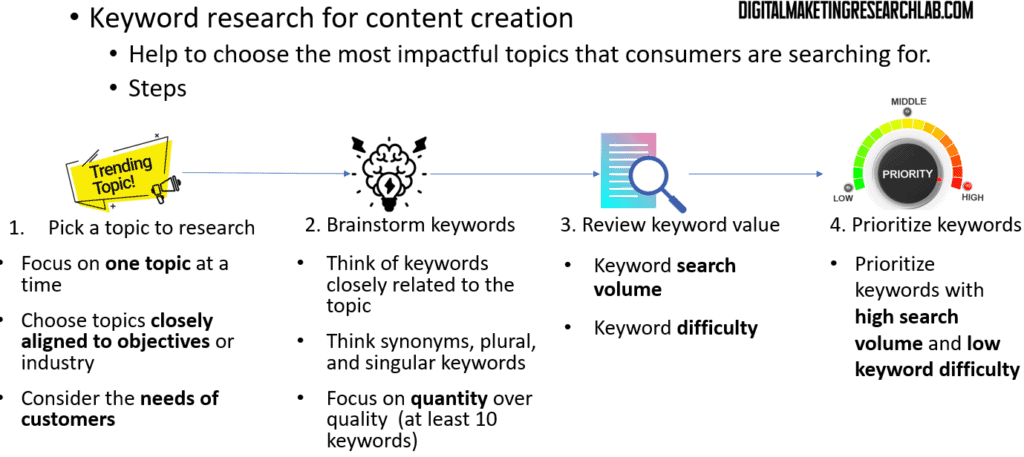
Doing thorough keyword research is the foundation of an effective SEO content strategy. Here are the key steps:
1. Pick a topic to research – Focus on one theme or subject area at a time, and have a specific web page in mind.
2. Brainstorm related keywords – Generate a list of terms and phrases, including synonyms, plurals, and long-tail variations.
3. Review keyword value – Analyze search volume, competition, and relevance for each keyword.
4. Prioritize the keywords – Identify your primary, secondary, and tertiary keywords to focus on.
This keyword research process helps you uncover the topics and queries that your target audience is actively searching for. You can then create content optimized around those high-value keywords.
Optimizing organic search ranking
Ok, Let’s discussing strategies for optimizing your website’s organic search ranking. Let’s dive right in.
Technical search engine optimization focuses on optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve its crawlability and indexability. This includes ensuring your site loads quickly, is mobile-friendly, and uses HTTPS for secure communication.

On-page optimization involves directly optimizing the content and HTML elements on your web pages. This includes optimizing the title tags, meta descriptions, headings, body copy, images, and URLs. The goal is to make your pages as relevant and engaging as possible for users.
Pre-click optimization refers to elements that are visible to users before they click on your search result, like the title tag, URL, and meta description. The aim here is to entice users to click through to your site.
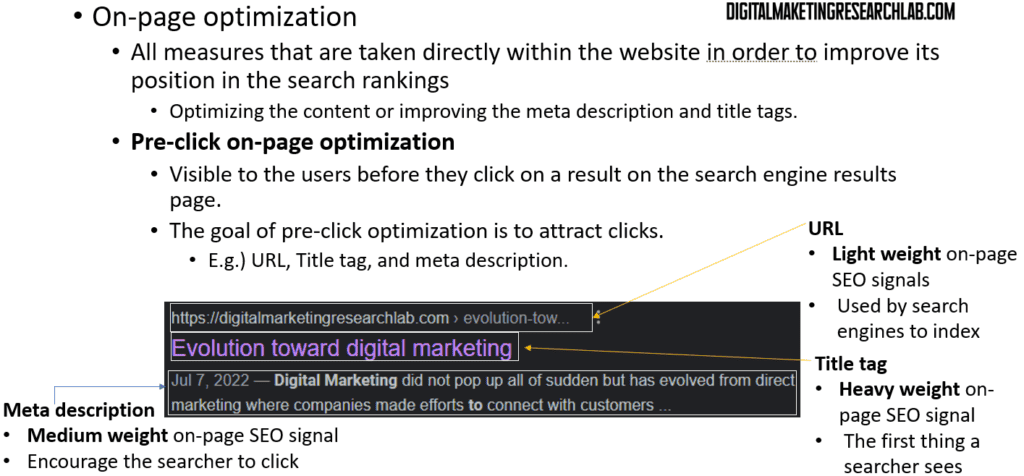
URLs are a lightweight on-page signal. Keep them short, include your target keyword, use dashes and lowercase letters, and stick to around 70 characters.
Title tags are a critical on-page element. They should include your target keywords, position them near the beginning, and keep the length to around 55 characters. The title should also be descriptive and compelling for users.
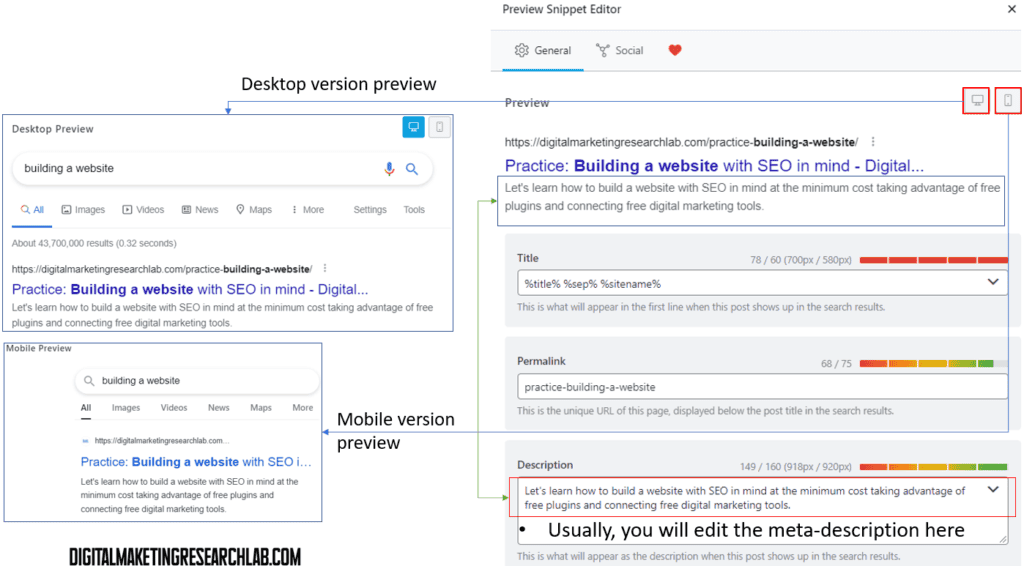
Meta descriptions are the short snippets of text that appear under your title in search results. They should be 2 concise sentences at most, 156 characters max for desktop and 115 for mobile. Focus on making them engaging and including your primary keyword.

If you already built your own website and activated Rank Math, you can find following features to optimize organic search ranking.
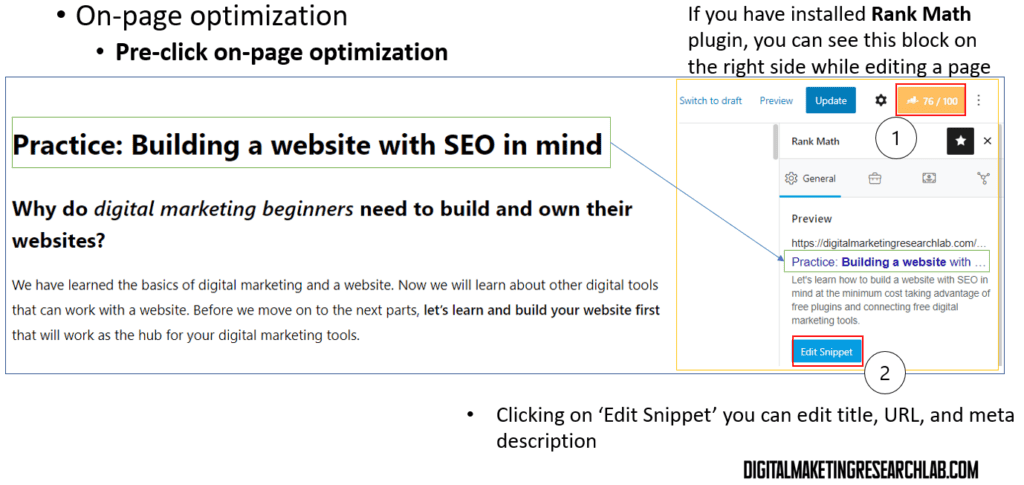
With the features, you can take a preview of desktop version and mobile version Also, you can edit the meta-description here.
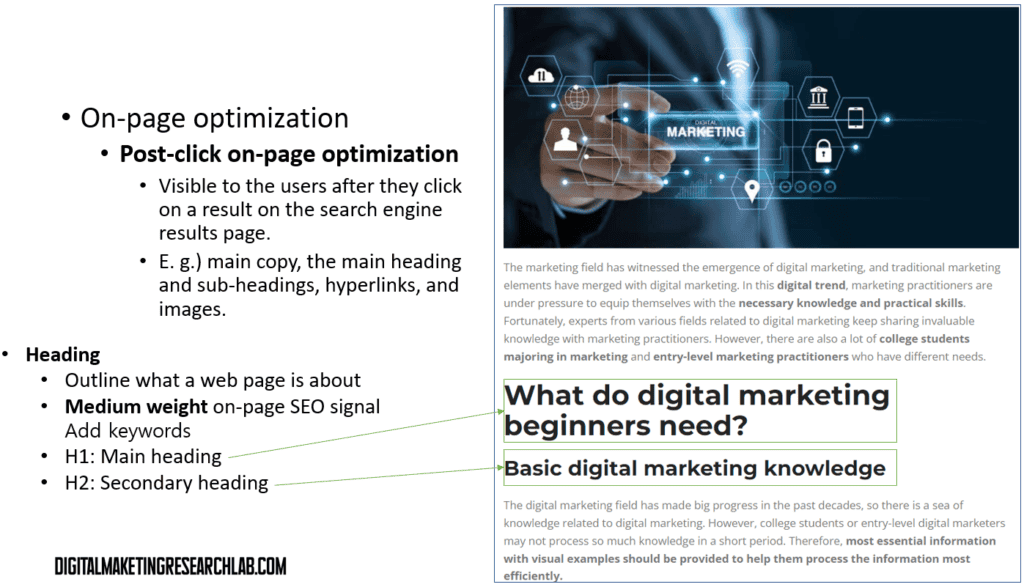
Optimizing headings in a logical hierarchy, with the main H1 heading, followed by H2 and H3 subheadings. Include relevant keywords where it makes sense, but avoid keyword stuffing.
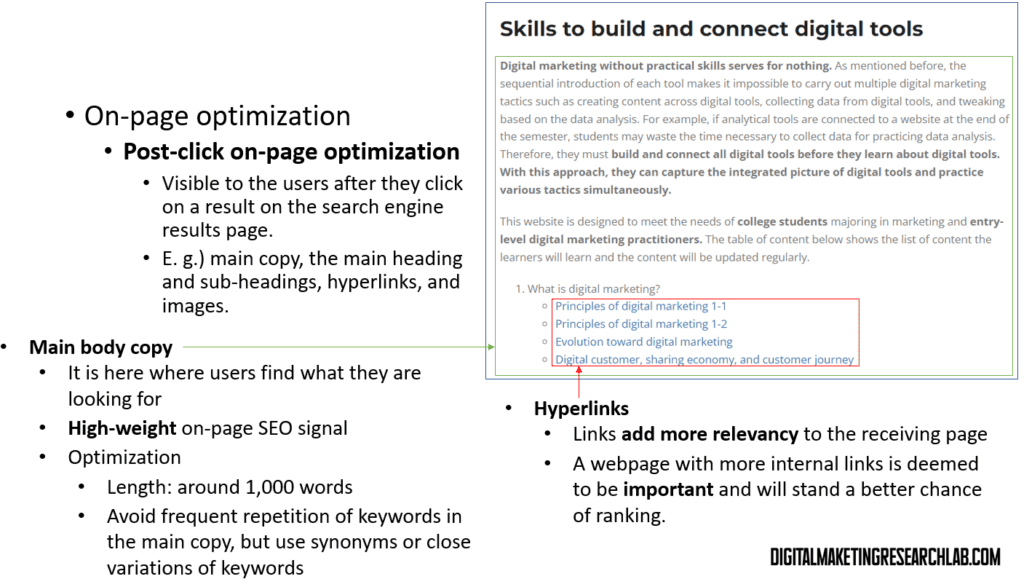
Your main page content is a high-weight on-page signal. Aim for around 1,000 words, use synonyms and variations of keywords rather than repetition, and ensure it provides a great user experience.
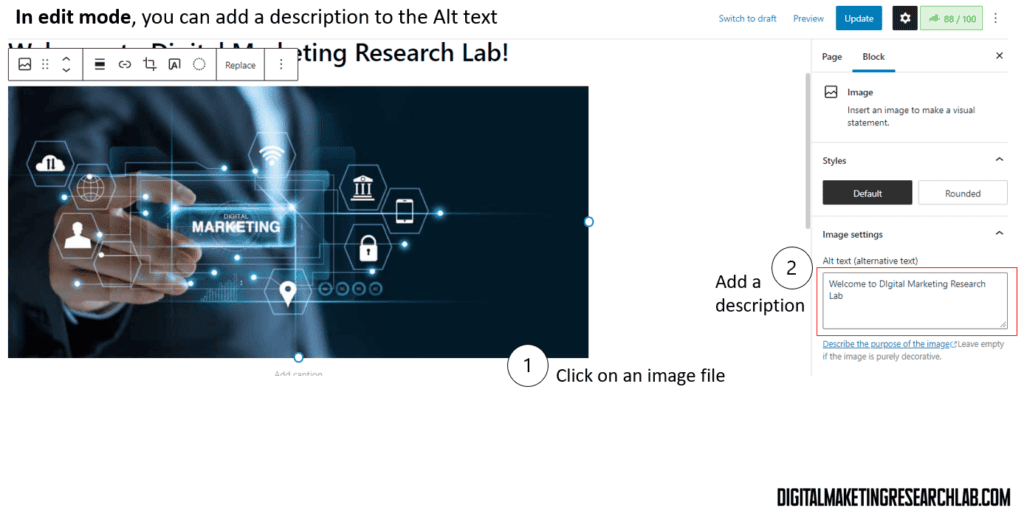
Images are a lightweight on-page signal. Be sure to use descriptive alt text, meaningful filenames, and web-friendly file formats like JPG and PNG.

If you already built your own website and activated Rank Math, you can add a short description here
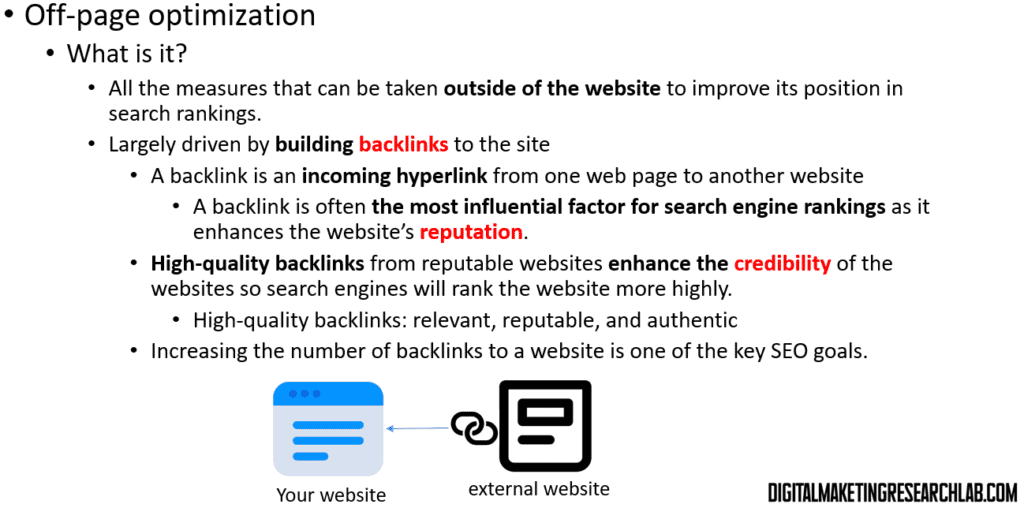
Off-page optimization refers to activities outside your website that can improve its search rankings, primarily building high-quality backlinks from reputable sites. This helps establish your site’s credibility and authority.
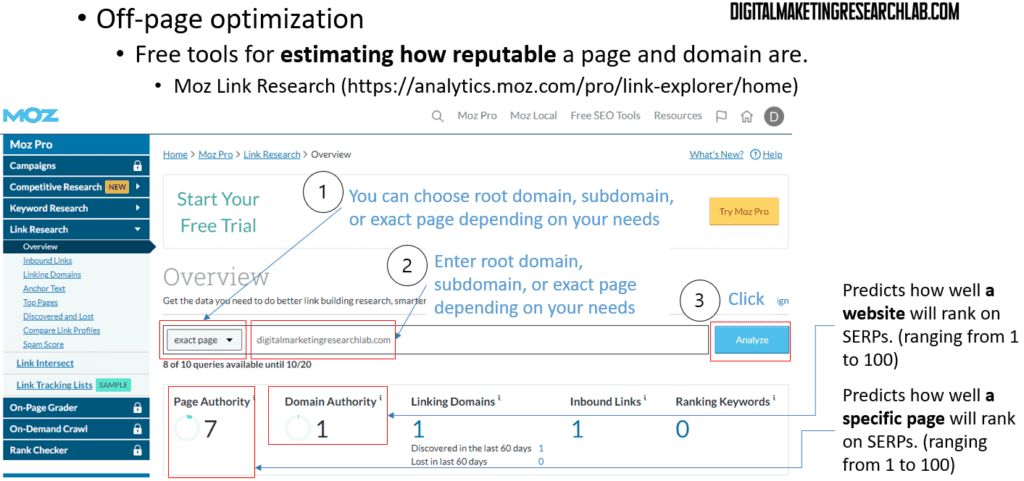
You can use free tools for estimating how reputable pages or a domain are. Try Moz Link Research and follow the steps in the picture below and see how reputable your domain is.
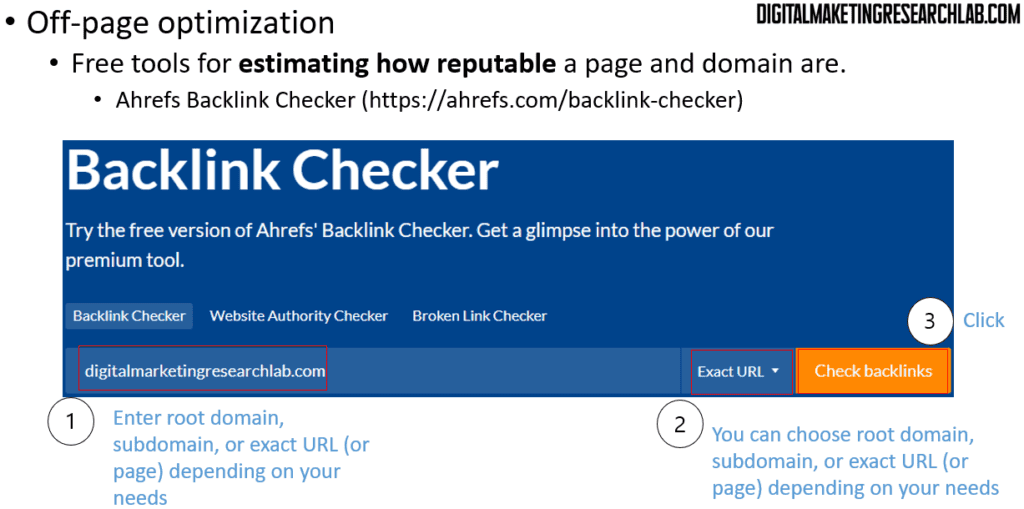
You may also try Ahrefs Backlink Checker.
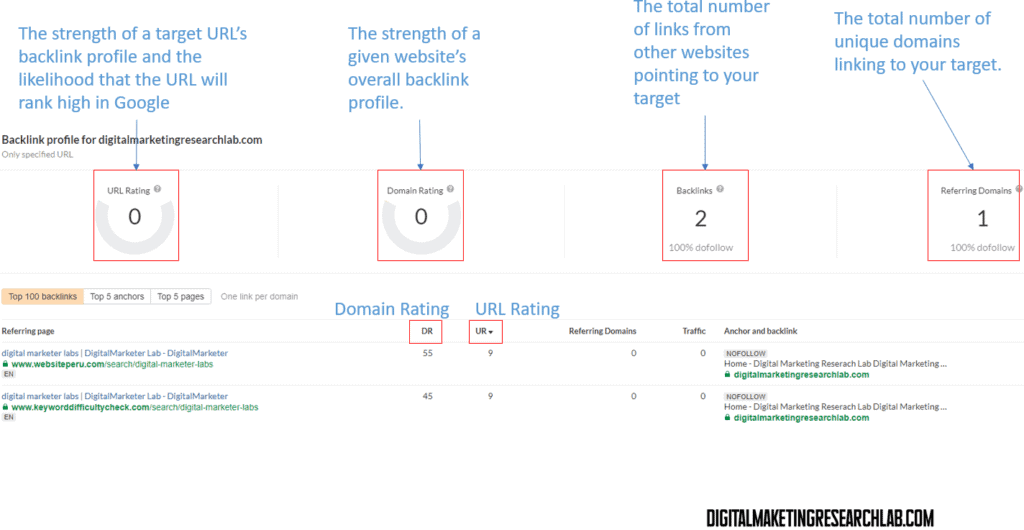
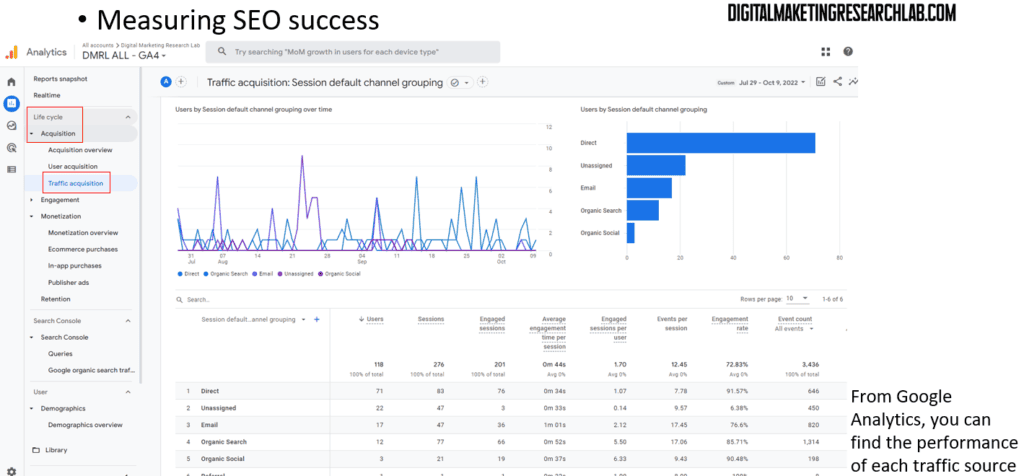
To measure the success of your SEO efforts, track metrics like keyword rankings, organic website traffic, conversions/sales, referral traffic, and backlink growth. Tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console can provide valuable data.
As you already connected your website with GA4, you can see some relevant metrics
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.

