A new era
Digital Marketing did not pop up all of sudden but has evolved from direct marketing where companies made efforts to connect with customers on a one-on-one basis.
Web 1.0 was an online version of direct marketing without interactions (i.e., one-way communication)so it wasoftenreferred to as the ‘read only’ web. Organizations shared brochures online with basic shopping carts. One of the major benefits was disintermediation where barriers between customers and companies are removed. Web 2.0 emerged as technology advanced, allowing two-way communication and interactive marketing. Many newly launched social media networks accelerated Web 2.0 enabling customers to add comments directly and instantly to company content.
Web 3.0 was introduced as online technology made it possible to find meaning in the content, which was known as the semantic web. Web 3.0 can process information using technologies like machine learning (ML) and big data. Web 3.0 is said to enable digital marketing.
Although a formal version of Web 4.0 has not been clearly defined, it is considered part of the Internet of Things (IoT). Web 4.0 is characterized by the seamless connection among devices through WiFi, and data from IoT devices drive customer insights.
Digital people
The advance in technology has brought in digital natives who were born after 1980. They are familiar with digital devices as they have grown up in a time when mobile phones, tablets, and wearables are the norm. In contrast, those born before 1980 are considered digital immigrants, and they are relatively new to this technology and struggle to learn how to use new technology.
Although we are living in a digital era, not all equally benefit from digital technology as represented by the term digital divide – a gap between those who have access to digital technology and those who do not. Some may not access the internet properly because they live in remote areas. Some may not use the technology because they have not learned or are reluctant to learn how to use it. Others may not have enough money to access the technology.
Digital products & places
With data stored in the cloud, cloud computing has enabled software and services to run on the internet, and thus, customers can access digital technology at any time in any location. These days, we access my programs at are cloud-based such as Office365, Dropbox, Netflix
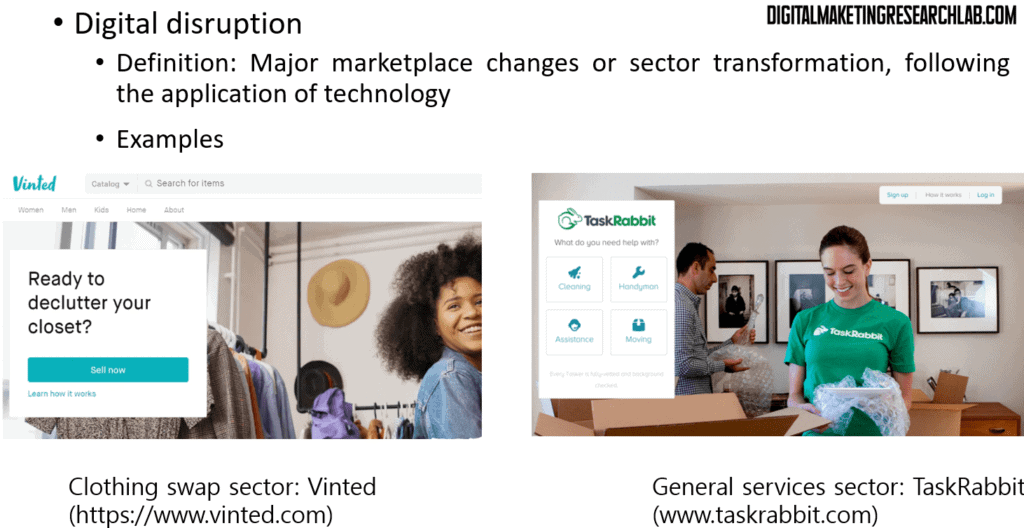
Digital technology has disrupted various industries by replacing outmoded products and services. Digital disruption can be defined as major marketplace changes or sector transformation, following the application of technology.
For example, Airbnb has emerged as a strong competitor to hotels in the accommodation section with its P2P-based services via a digital app. In the car rental section, Zipcar is competing with traditional car rental companies by adopting a digital-first approach: booking via an app as well as allowing one to rent a car by the hour.

For the clothing swap sector, Vinted is replacing the traditional practice of swapping clothing with friends. Even for general services sectors, TaskRabbit connects people in need of a certain type of service (e.g., house cleaning) with those who are capable of such services. In such a way, TaskRabbit encroaches on the traditional service exchanges among local people. Both Vinted and TaskRabbit are app-based services.
Digital payments and process
The advance in digital commerce (or e-commerce) has stimulated the online payment system on top of the usage of credit cards. Paypal is an online payment system offering an e-money function and supporting peer-to-peer payment. In addition, Alipay, Google Pay, and Apple Pay have been introduced to serve as digital wallets and can be used for contactless payments offline. Furthermore, the social network payment systems, implemented by WeChat, Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, or Messenger, are expected to facilitate online shopping.

Digital data acquisition
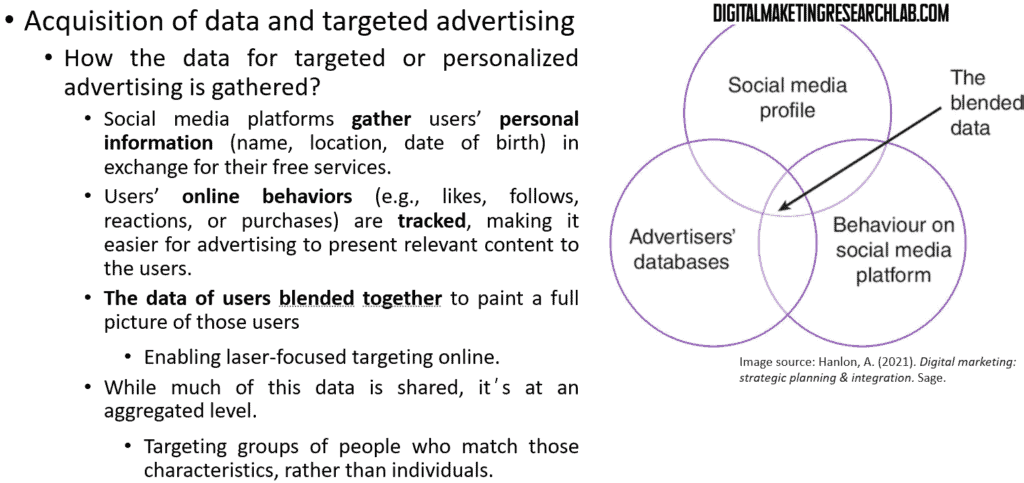
In the digital environment, the acquisition of data is essential for targeted content and advertising to maximize marketing-related performance. Then, how the data for targeted or personalized advertising is gathered? First of all, social media platforms gather users’ personal information, such asname or location, in exchange for their free services. In addition, users’ online behaviors, such as likes, follows, reactions, or purchases, are tracked, making it easier for advertising to present relevant content to the users.
These data and advertisers’ databases are blended together, painting a full picture of those users which enables laser-focused targeting online. While much of this data is shared, it’s at an aggregated level. Thus, advertisers and marketers can target groups of people who match those characteristics, rather than individuals, which can contribute to protection of individual privacy.
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.

