Welcome to Email Marketing. In this chapter, we’ll explore the fundamentals, strategies, and best practices of email marketing in the digital age.
Email marketing fundamentals
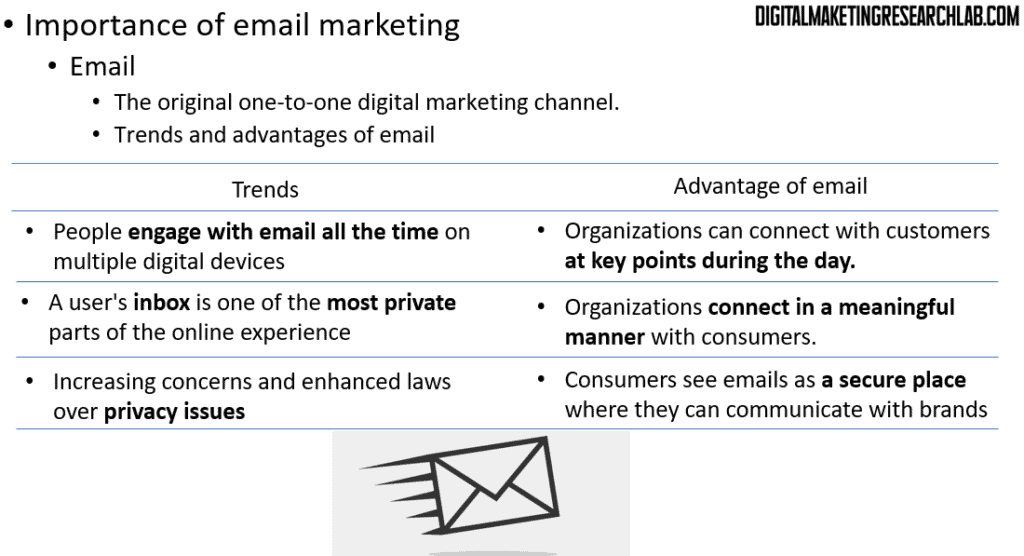
Let’s begin by discussing the importance of email marketing. Email remains the original one-to-one digital marketing channel, and its significance has only grown over time.
There are several key trends and advantages that make email marketing so effective. First, people engage with email constantly throughout the day on multiple devices. This gives organizations the opportunity to connect with customers at crucial touchpoints. Second, a user’s inbox is one of the most private spaces in their online experience. This allows brands to connect with consumers in a meaningful and personal way. Lastly, with increasing concerns over privacy issues and new regulations, consumers view email as a secure channel for communication with brands they trust.
The effectiveness of email marketing is supported by impressive statistics: 64% of decision-makers use email as a primary communication tool. The return on investment for email marketing is higher than any other marketing channel. Email marketing converts three times better than social media. And perhaps most importantly, 44% of consumers who receive targeted emails report buying at least one item as a result. These numbers clearly demonstrate why email remains a crucial component of any digital marketing strategy.

To maximize the impact of email marketing, it’s important to understand the five levels of audience engagement campaigns. The first level is Foundational. These are basic communications sent to the broadest audience, including newsletters, bulletins, holiday greetings, and company or product announcements.
The second level is Promotional. These emails are designed to generate revenue or product demand. Examples include sales announcements, special offers, discounts, and holiday shopping promotions.
The third level is Informational. These emails aim to establish and grow relationships with customers. They might include product-related education, how-to guides, articles, and lead nurturing programs.

Informational Campaigns: These communications strengthen customer relationships by providing value. Examples include product education, how-to guides, articles, and lead-nurturing sequences.

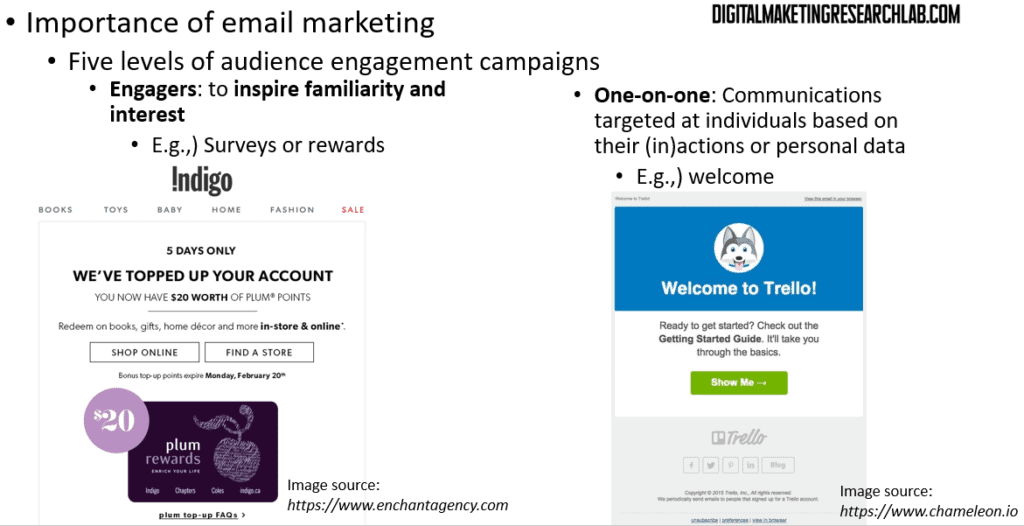
The fourth level is Engagers. These emails are designed to inspire familiarity and interest among subscribers. Examples include surveys or reward programs.
The fifth and final level is One-on-one. These are highly targeted communications based on individual actions, inactions, or personal data. Welcome emails are a common example of this type.
As you progress through these levels, your email campaigns become more specific and personalized, potentially leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
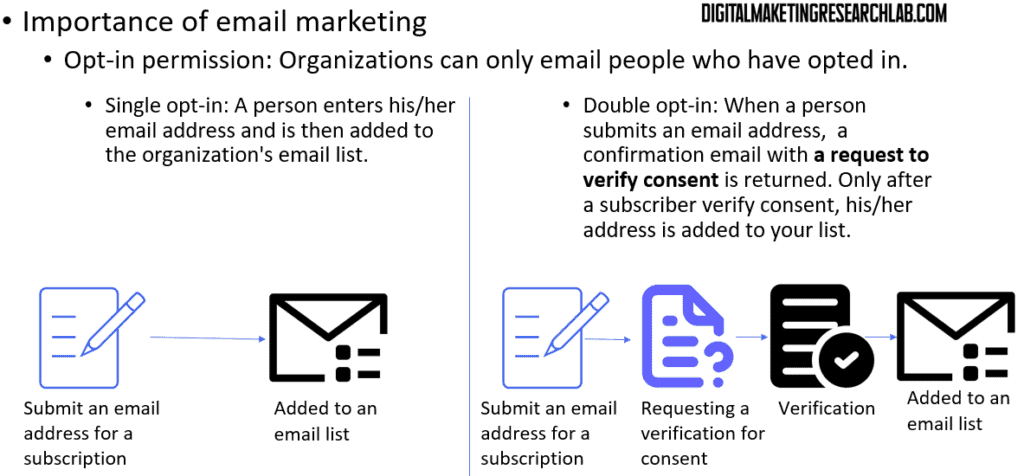
Now, let’s discuss a critical aspect of email marketing: opt-in permission. It’s crucial to remember that organizations can only email people who have explicitly opted in to receive communications.
There are two main types of opt-in. Single opt-in occurs when a person enters their email address and is immediately added to the organization’s email list.
Double opt-in involves an additional step. After a person submits their email address, a confirmation email is sent with a request to verify consent. Only after the subscriber verifies their consent is their address added to the list.
Let’s compare single opt-in and double opt-in methods:
Single opt-in offers a smoother user experience and allows for rapid growth of your email list. However, it prioritizes quantity over quality.
Double opt-in, while potentially slowing down list growth, ensures higher-quality subscribers. It confirms that people are entering real email addresses and genuinely want to receive your communications.
The choice between these methods often depends on your specific business needs and the nature of your audience.

Moving on to the legal aspect of email marketing, it’s crucial to understand the regulations in place. These laws are designed to protect users from fraud and give them control over their email permissions.
There are four primary pieces of legislation that every email marketer must be familiar with. First is the General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, introduced by the European Union in 2018. It requires explicit consent from a person to receive marketing emails.
Second is the California Consumer Protection Act, or CCPA, introduced in 2020. While similar to GDPR, it includes some differences, such as opt-outs to prevent companies from selling consumer data to third parties.
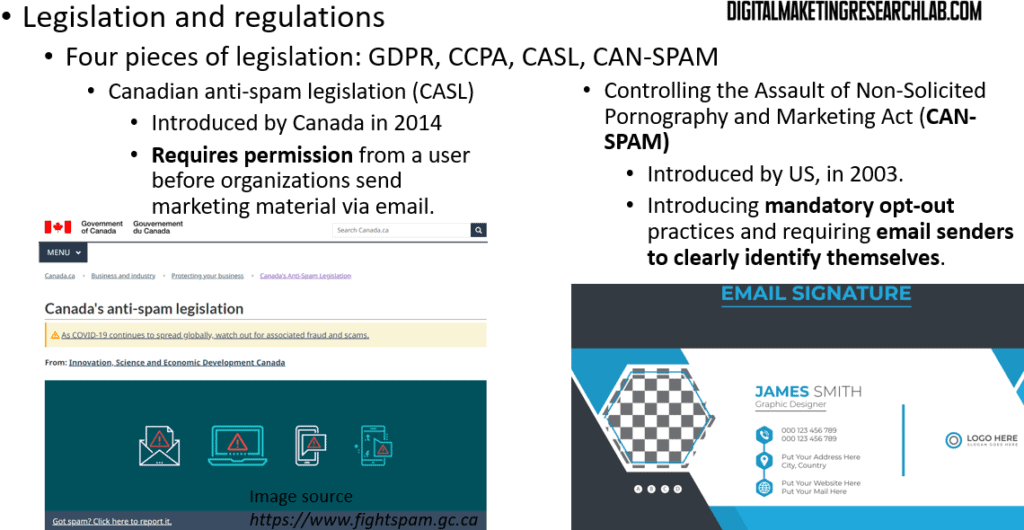
The third important regulation is the Canadian Anti-Spam Legislation, or CASL, introduced in 2014. Like GDPR, it requires permission from a user before organizations can send marketing material via email.
Lastly, we have the CAN-SPAM Act, which stands for Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing Act. Introduced in the United States in 2003, it established mandatory opt-out practices and requires email senders to clearly identify themselves.
Understanding and complying with these regulations is crucial for any organization engaged in email marketing, especially if you have an international audience.
Email marketing tools and strategy
ANow, we are moving on to email marketing tools and strategy. First of all, let’s discuss the key elements for an effective email strategy.
The first element is segmentation. This involves grouping similar users together and sending relevant messages to targeted segments. By tailoring your content to specific groups, you can significantly increase engagement and conversion rates.
The second element is personalization. This goes beyond simply addressing customers by their name. It involves offering personalized recommendations based on their past behavior or preferences.
The third element is timing. It’s crucial to deliver the right message at the right time for customers. This might involve considering factors such as time zones, typical work hours, or even individual user habits.
By focusing on these three elements—segmentation, personalization, and timing—you can create more effective and impactful email campaigns.

An essential tool for managing email campaigns is an Email Service Provider, or ESP. These platforms offer a range of features to streamline your email marketing efforts.
Some popular ESPs include Mailchimp, which is known for its user-friendly interface and robust features for small to medium businesses; Aweber, which offers strong automation capabilities; Constant Contact, which is particularly effective for event management and social media integration; and GetResponse, which provides advanced features like webinar hosting alongside email marketing tools. Each of these platforms has its strengths, so it’s important to choose one that aligns with your specific needs and goals.
Let’s delve into some of the key features offered by Email Service Providers.
First, they provide contact database management. This allows you to store and manage your list of subscribers, email addresses, and other contact information efficiently.
Second, ESPs offer segmentation and personalization capabilities. Using the data in your contacts’ personal profiles, you can segment your audience and personalize your emails for better engagement.
Automation is a crucial feature. It allows repetitive tasks like sending welcome emails or purchase receipts to be handled automatically, saving time and ensuring consistency. ESPs also provide behavior tracking, offering data and insights about your recipients. This includes information on how many emails are successfully delivered and opened, which can help you refine your strategy over time.
Two more important features of ESPs are custom domains for email sends—which allow you to send emails using your own website URL to increase trust and brand recognition—and unsubscribe management, which automatically handles users who wish to opt out. This helps ensure compliance with regulations and respects your audience’s preferences.
These features combine to make ESPs powerful tools for managing and optimizing your email marketing efforts.

Now, let’s discuss email list growth and management, starting with lead generation.
Leads are people who could potentially become customers. Lead generation is the process of collecting email addresses from these potential customers. This is a crucial first step in building your email marketing list. By offering something of value in exchange for an email address, you create an opportunity to nurture these leads and potentially convert them into customers.
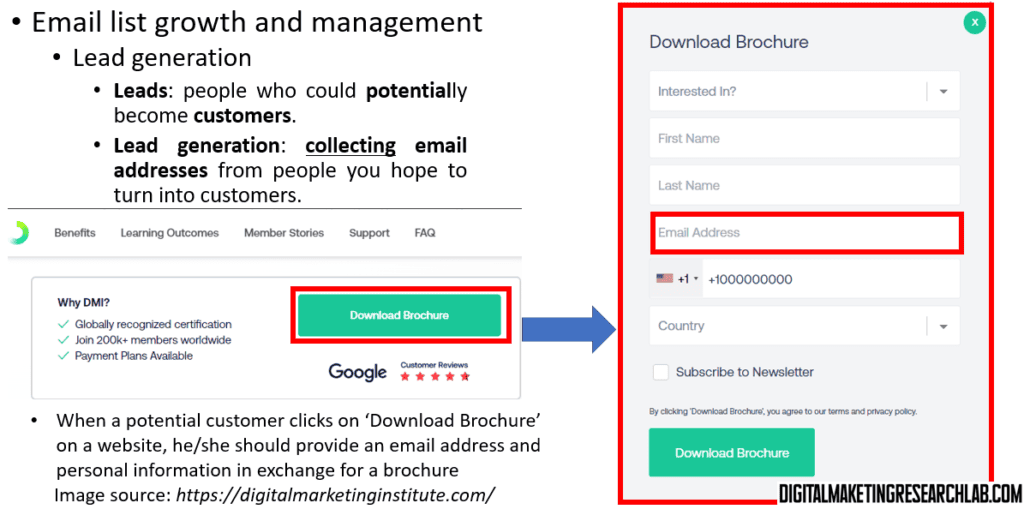
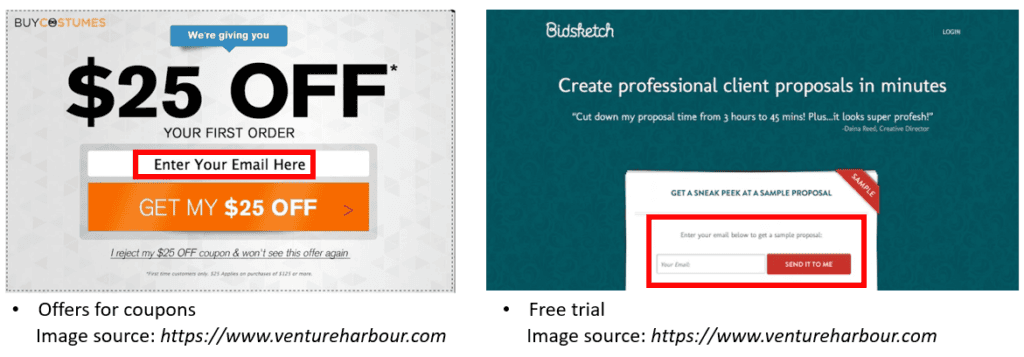
Once you’ve generated leads, the next step is lead nurturing. This involves emailing quality content to your leads—the potential customers you’ve collected through various campaigns and channels.
The goal of lead nurturing is to help these potential customers understand the value of your products or services. By providing useful, relevant information over time, you increase the likelihood of converting these leads into paying customers. This process is especially important in B2B contexts or for products with longer sales cycles, where customers may need more information and reassurance before making a purchasing decision.

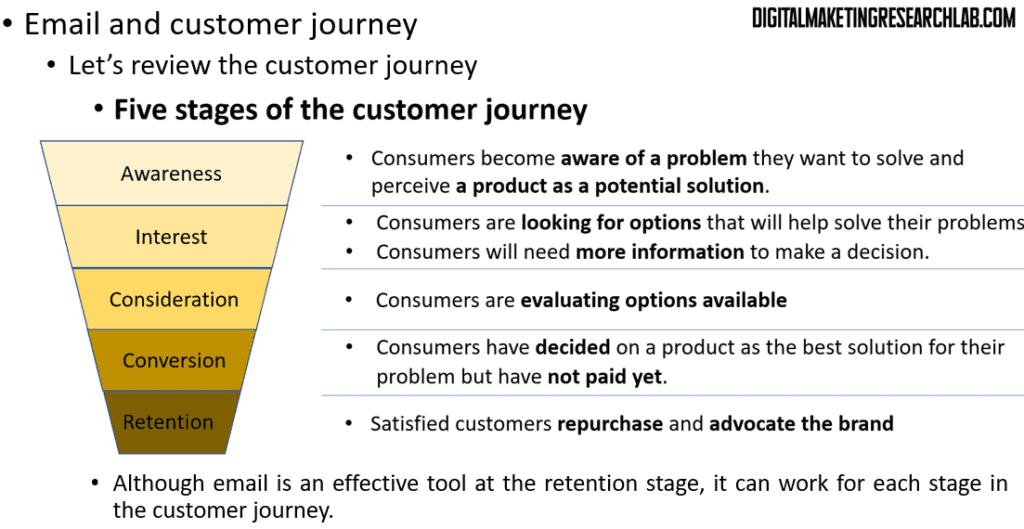
To effectively use email throughout the customer journey, it’s important to understand the different stages a customer goes through. Let’s review these stages:
The first stage is Awareness. Here, consumers become aware of a problem they want to solve and perceive a product as a potential solution. Next is the Interest stage. Consumers are actively looking for options that will help solve their problem and need more information to make a decision.
The third stage is Consideration. At this point, consumers are evaluating the options available to them. The fourth stage is Conversion. Consumers have decided on a product as the best solution for their problem but haven’t made the purchase yet.
Finally, we have the Retention stage. Here, satisfied customers repurchase and may even become advocates for the brand. While email is particularly effective at the retention stage, it can be a valuable tool at each stage of the customer journey when used strategically.
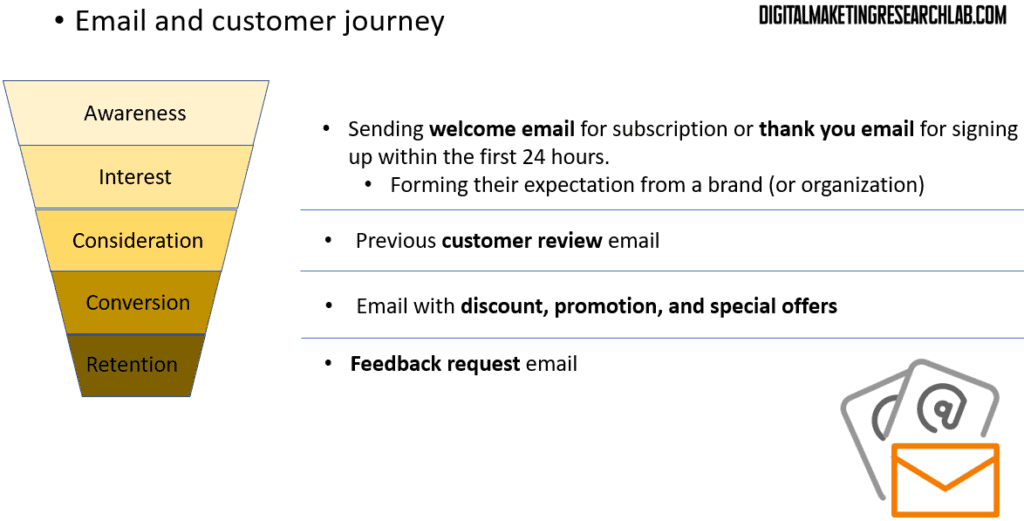
Let’s look at how email can be used effectively at each stage of the customer journey. In the Awareness and Interest stages, sending a welcome email for subscription or a thank-you email for signing up within the first 24 hours can be very effective. This helps shape the customer’s initial expectations of your brand.
During the Consideration stage, emails featuring customer reviews can be powerful. They provide social proof and can help potential customers feel more confident about your product or service. For the Conversion stage, emails with discounts, promotions, and special offers can provide that final push to make a purchase.
In the Retention stage, feedback request emails can make customers feel valued and provide you with meaningful insights. They also keep your brand top of mind for repeat purchases.
By tailoring your email content to each stage, you can guide customers through their journey more effectively.
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.

