Designing a website
We have explored a website and its components, such as main pages and supporting pages. Now, it is time to learn the basics of designing a website. Broadly, there are four key components of website design: information architecture, design, content, and optimization.
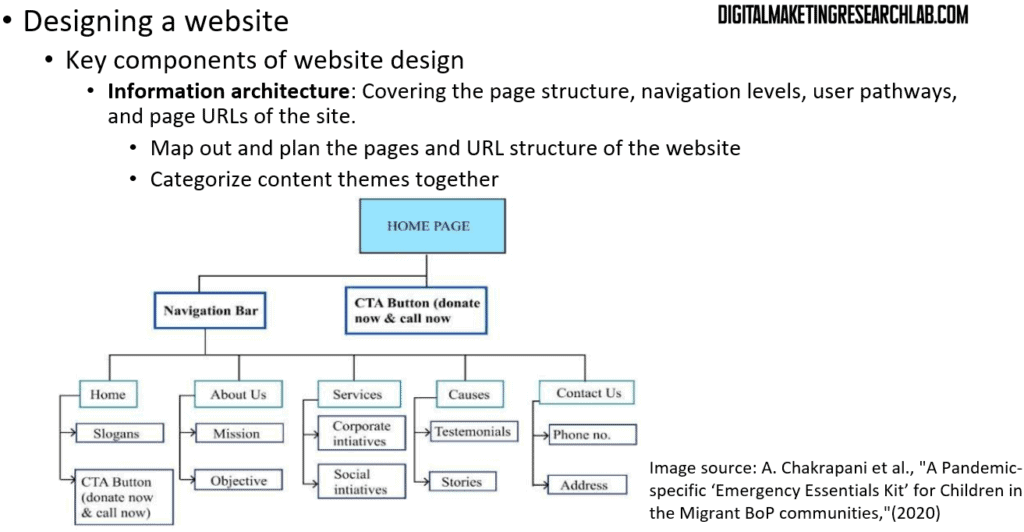
First, information architecture covers the page structure, navigation levels, user pathways, and page URLs of the site. To begin information architecture, a website designer needs to map out and plan the pages and URL structure of the website. Then, he/she categorizes content themes together.
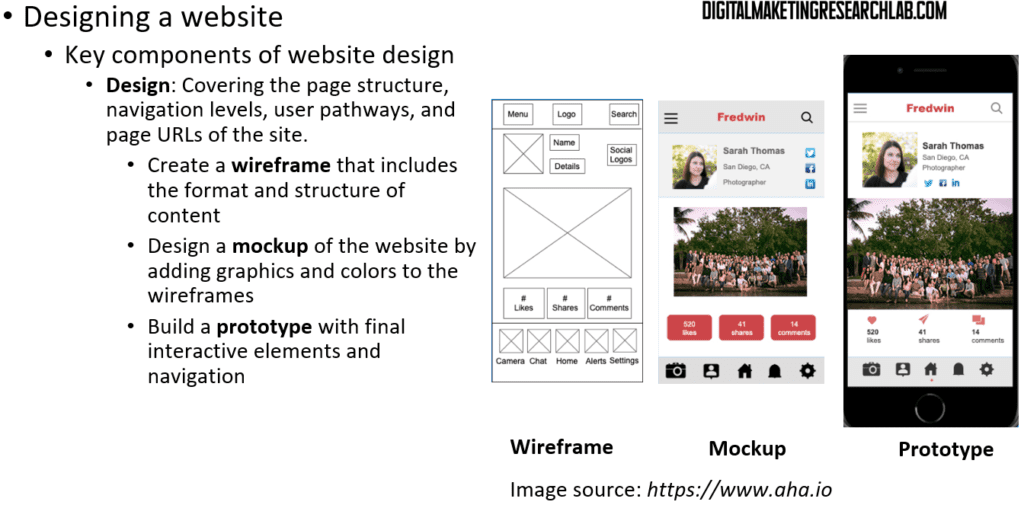
Next, website design covers the page structure, navigation levels, user pathways, and page URLs of the site. Regarding design, a web designer can start by creating a wireframe that outlines the format and structure of the content. Then, he/she can design a mockup of the website by adding graphics and colors to the wireframes. Finally, a web designer will build a prototype with final interactive elements and navigation.
Third, for website content, a content creator writes content, sources images for all pages, and adds content to the website.
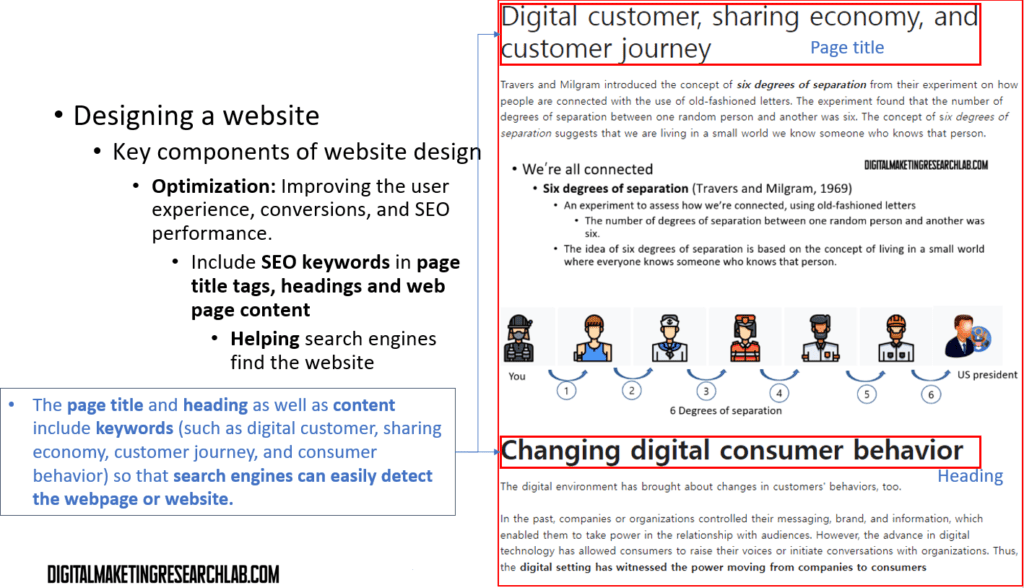
Finally, optimization can improve user experience, conversions, and search engine optimization (SEO) performance. For optimization, a website developer first needs to include SEO keywords in page title tags, headings, and web page content. This will help search engines detect the website more easily. You can see an example from a post ‘Digital customer, sharing economy, and custoerm journey’ on this website.
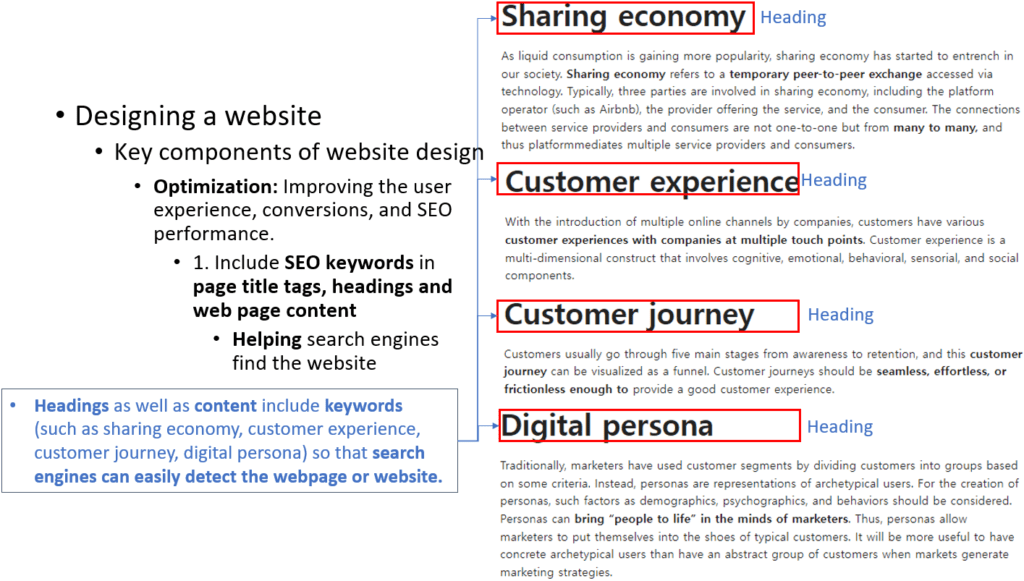
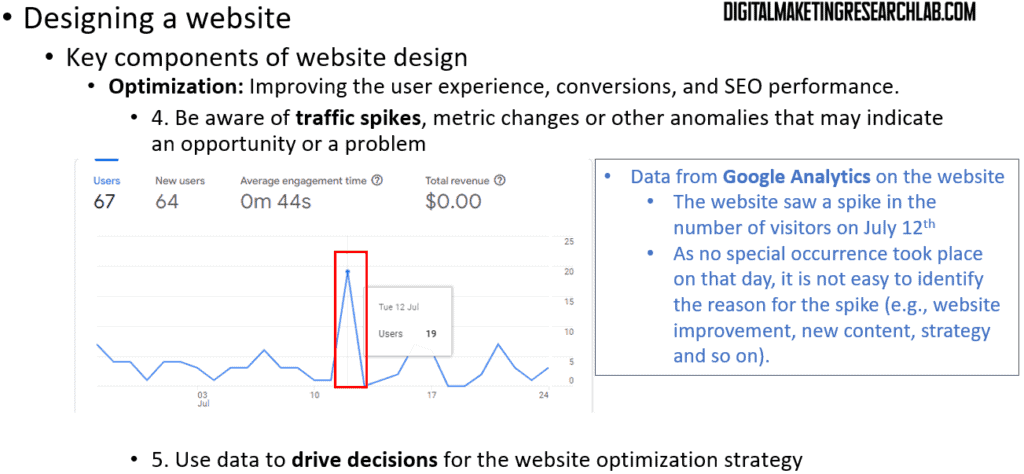
Next, after adding SEO keywords, a web developer or marketer needs to report on visitor engagement using website analytics tools. Then, they need to identify friction points through conversion funnels and goal tracking.
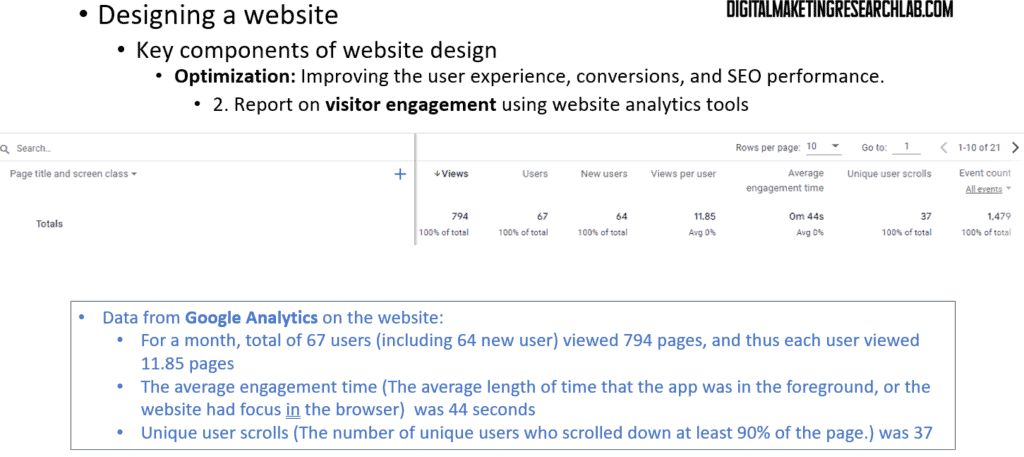
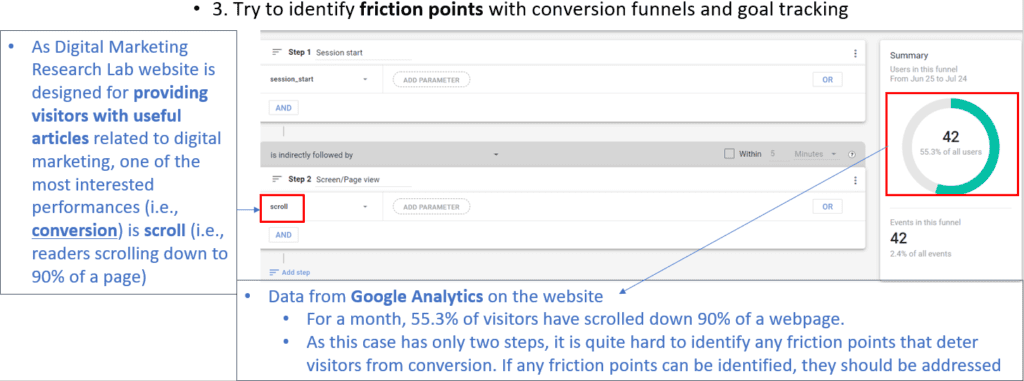
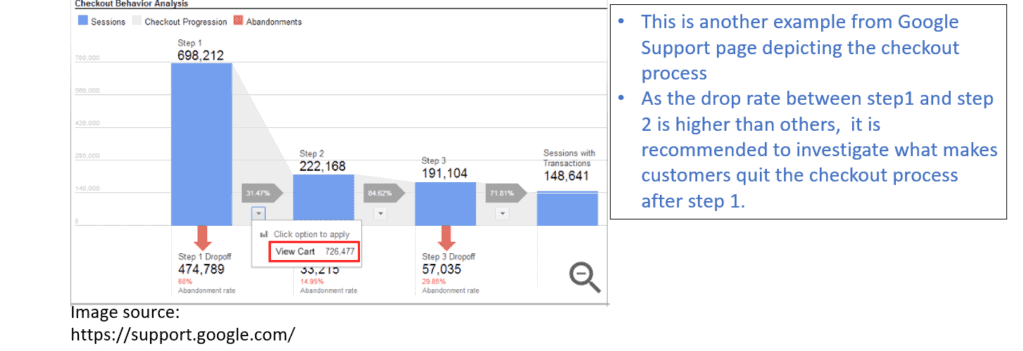
Also, attention should be paid to traffic spikes, metric changes, or other anomalies that may indicate an opportunity or a problem. Lastly, a marketer needs to use data to drive decisions for the website optimization strategy.
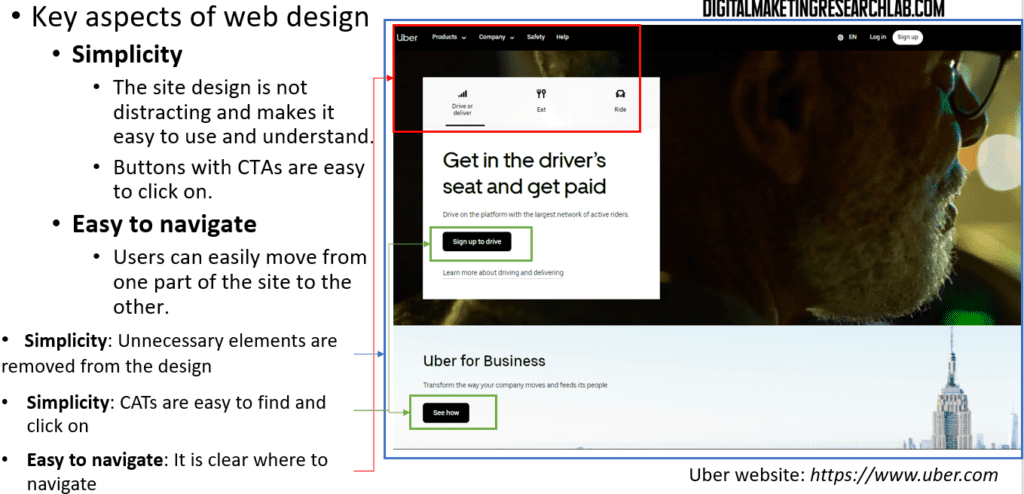
There are some key aspects of web design to remember: simplicity, ease of navigation, consistent information, and cohesive design.
Simplicity means that a site’s design is not distracting and is easy to use and understand. Buttons with CTAs should be easy to click. Easy to navigate means that users can move effortlessly from one part of the site to another.
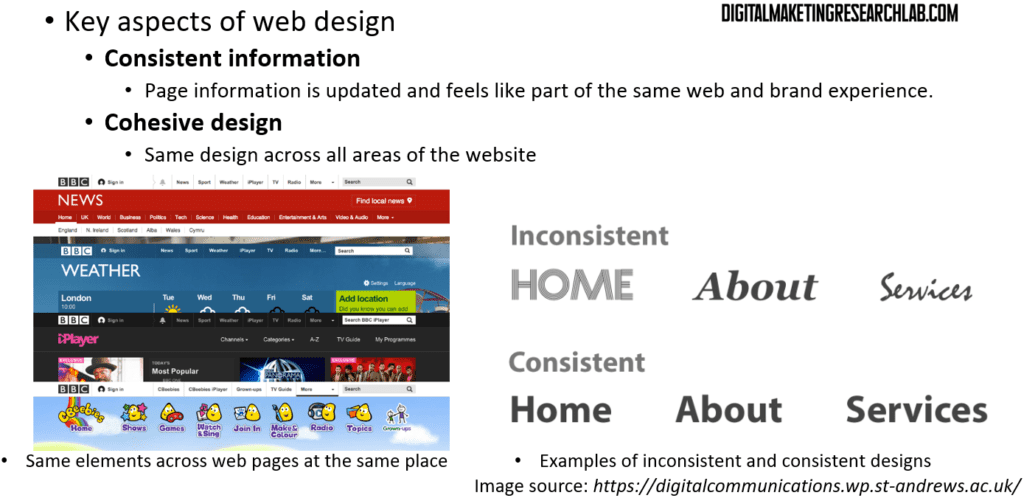
Consistent information means that page information is updated and feels like part of a unified web and brand experience. Cohesive design refers to having the same design across all areas of the website.
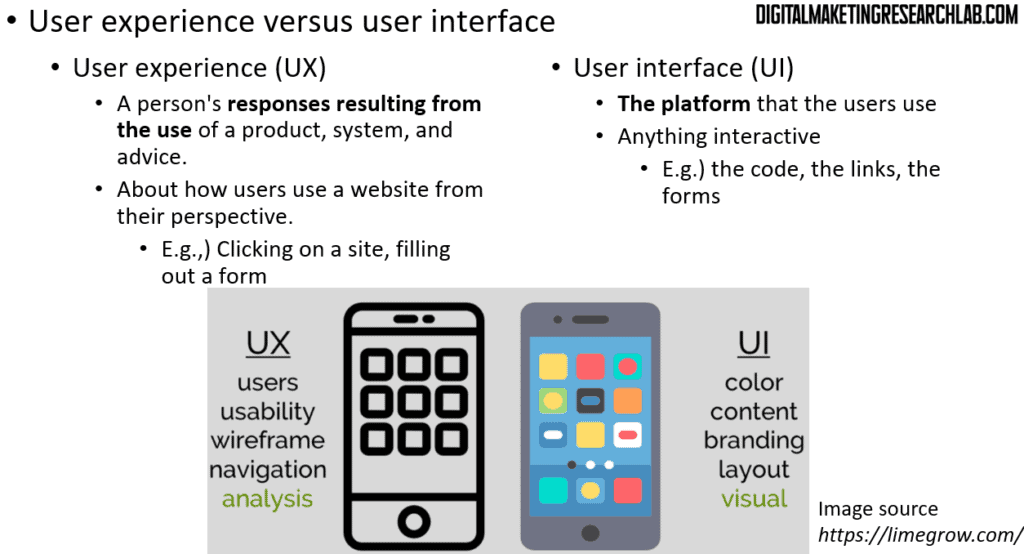
User experience and user interface
When it comes to website design, you need to understand two crucial terms: user experience (UX) and user interface (UI). User experience (UX) is a person’s responses resulting from the use of a product, system, or device. It concerns how users interact with a website—such as clicking on a site or filling out a form—from their perspective.
Meanwhile, user interface (UI) is the platform that users interact with. Anything interactive falls under UI, such as code, links, and forms.
There are five key principles for UX and UI: accessibility, clarity, learnability, credibility, and relevancy.
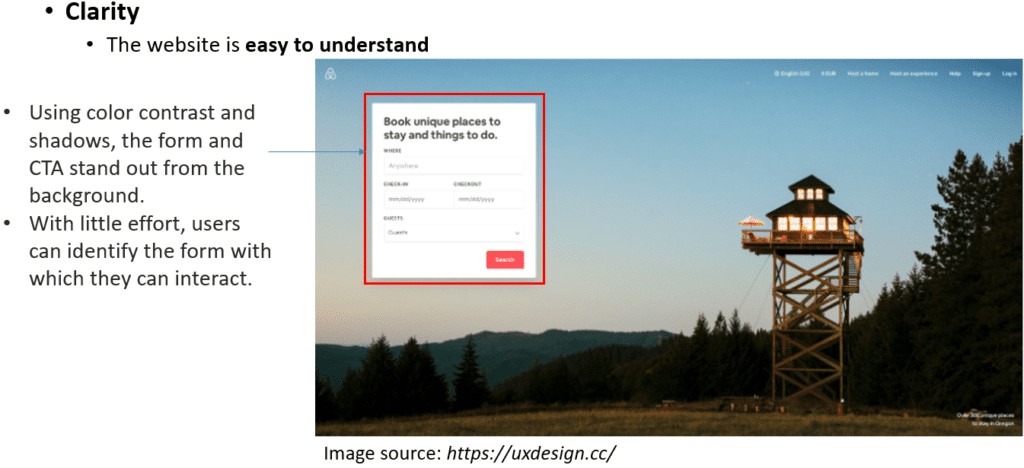
First, when a website has high accessibility, it is easy for any user to use, including those with vision or mobility issues. Second, when a website has high clarity, it means the website is easy to understand.

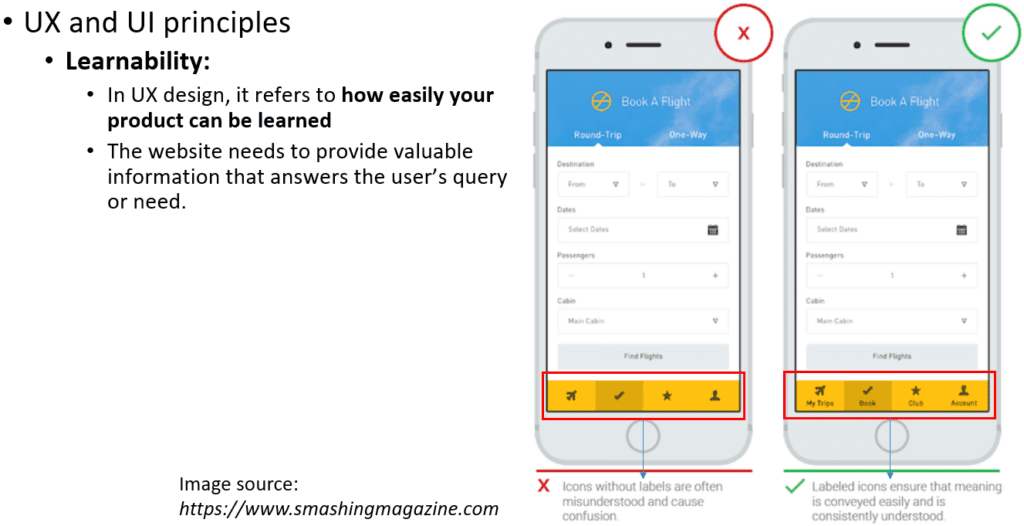
Third, learnability refers to how easily your product can be learned. A website needs to provide valuable information that answers the user’s query or need in a simple, accessible way.
Fourth, with regard to credibility, a website should use reliable information from reputable sources to prove its point or educate the user. Other factors that can improve credibility include design quality, upfront disclosure, current information, and connectedness to the rest of the web.
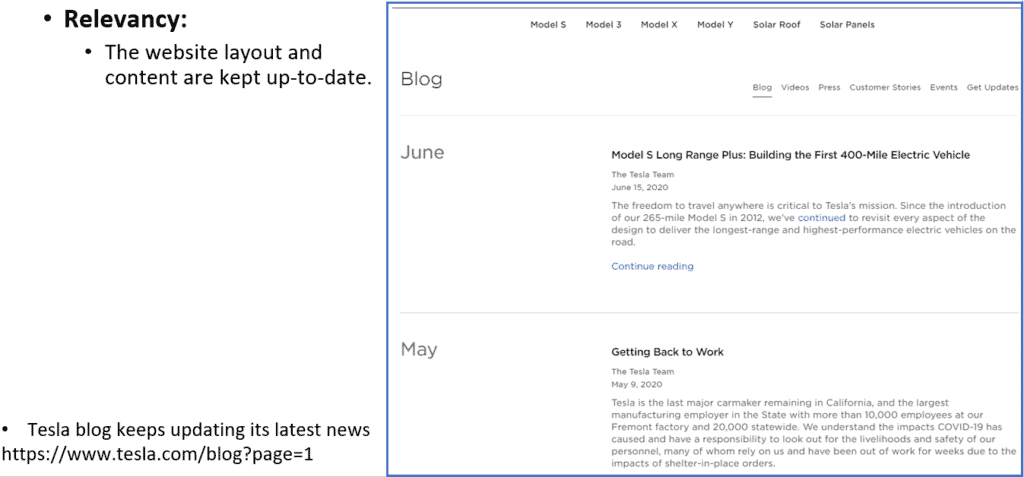
Finally, when a website has high relevancy, the website layout and content are kept up to date.

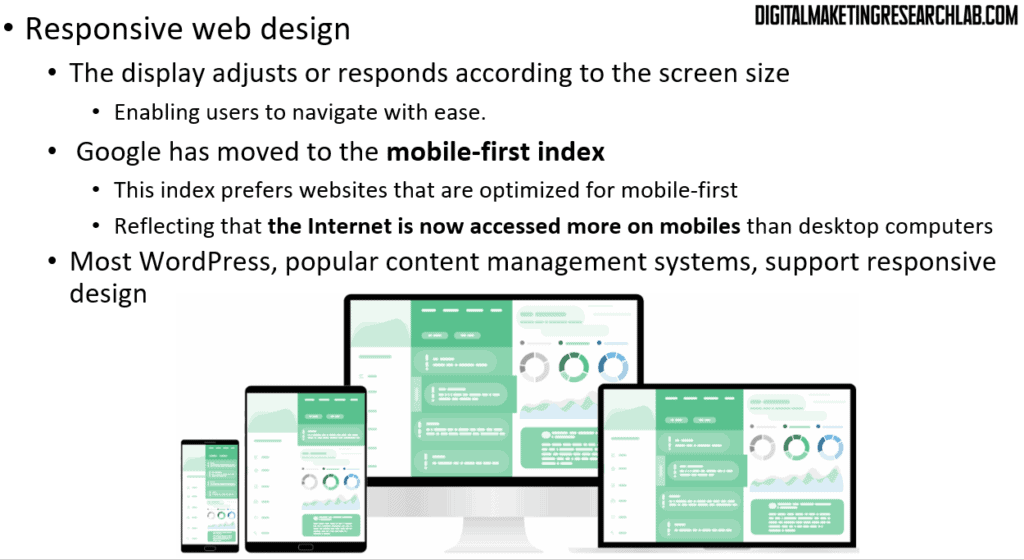
Responsive web design
Responsive web design means that the display adjusts or responds according to the screen size, which enables users to navigate with ease.
Recently, Google has moved to the mobile-first index. This index prefers websites that are optimized for mobile first, reflecting that the internet is now accessed more on mobile devices than desktop computers. These days, most WordPress themes, popular content management systems, support responsive design. This website is also built with WordPress, so you can see its display automatically adjust according to different devices.
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.

