Main pages of a website
A website has main pages such as a home page, about page, contact page, product category page, product page, checkout page, payment gateway page, lead-generation page, and supporting pages.
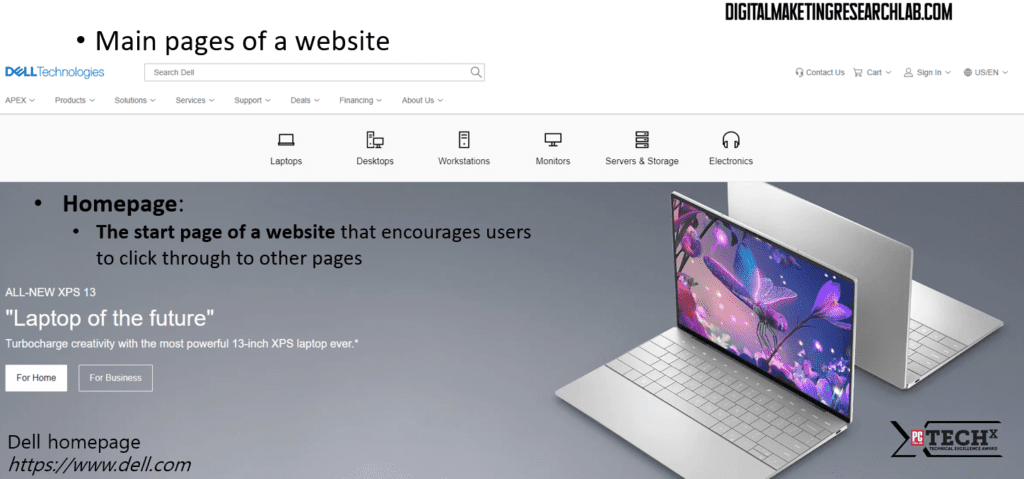
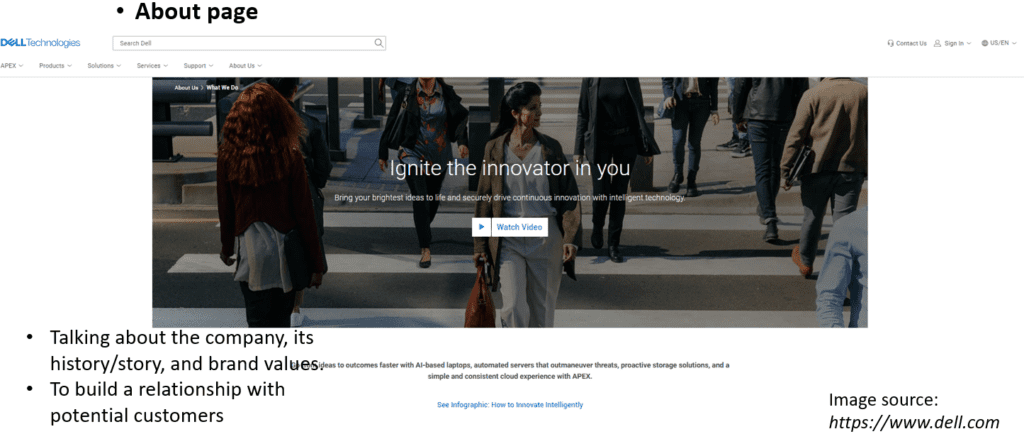
Let’s take the Dell website as an example. A home page is the starting point of a website and encourages users to click through to other pages. An about page talks about the company, its history or story, and its brand values. This page is usually designed to build a relationship with potential customers.
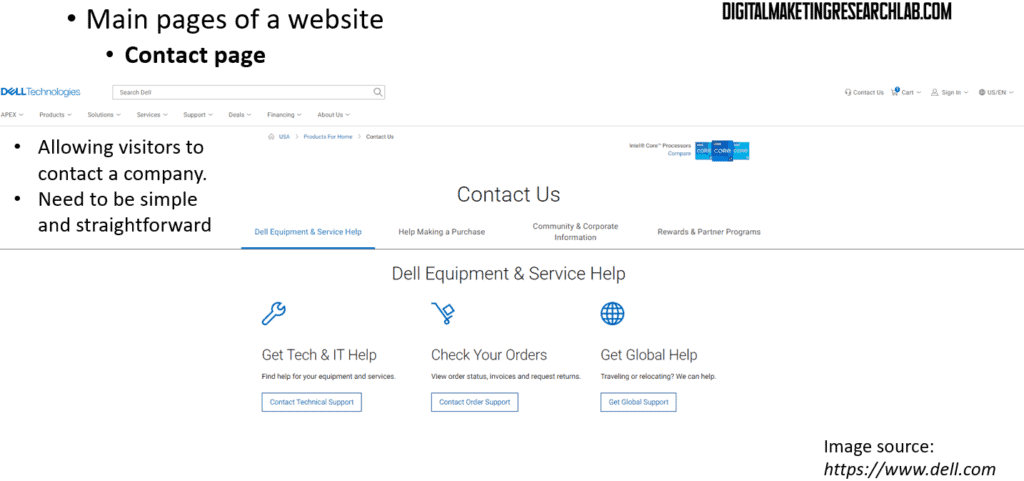
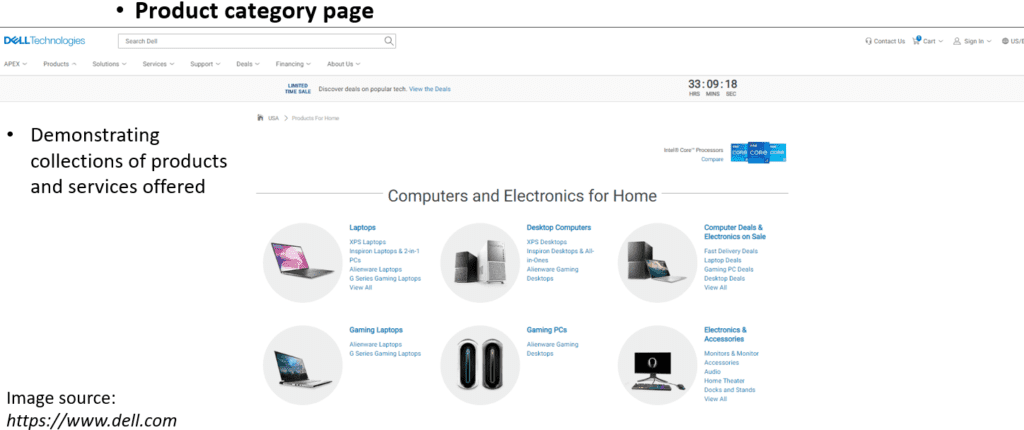
A contact page allows visitors to reach the company when they have opinions or, at times, complaints. This page should be simple and straightforward so visitors can easily make contact with the company. A product category page displays collections of products and services that the company offers.
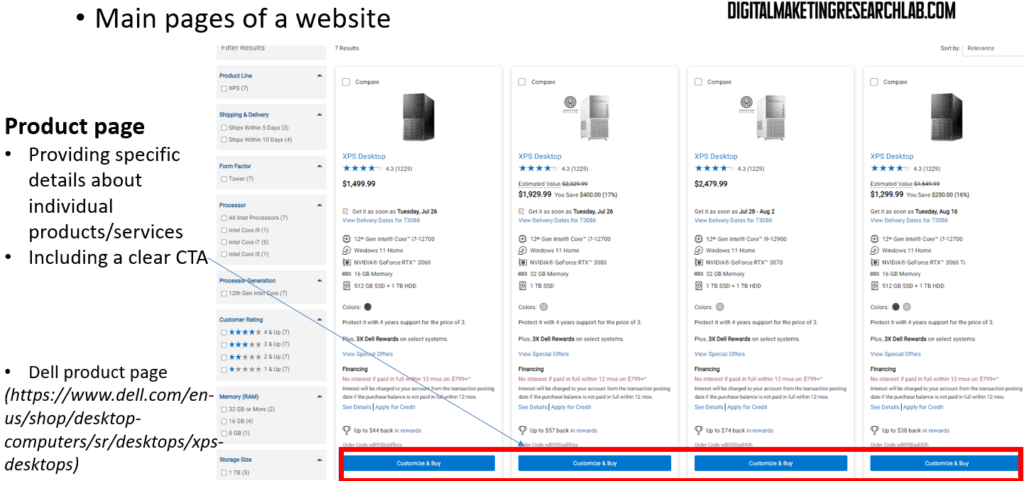
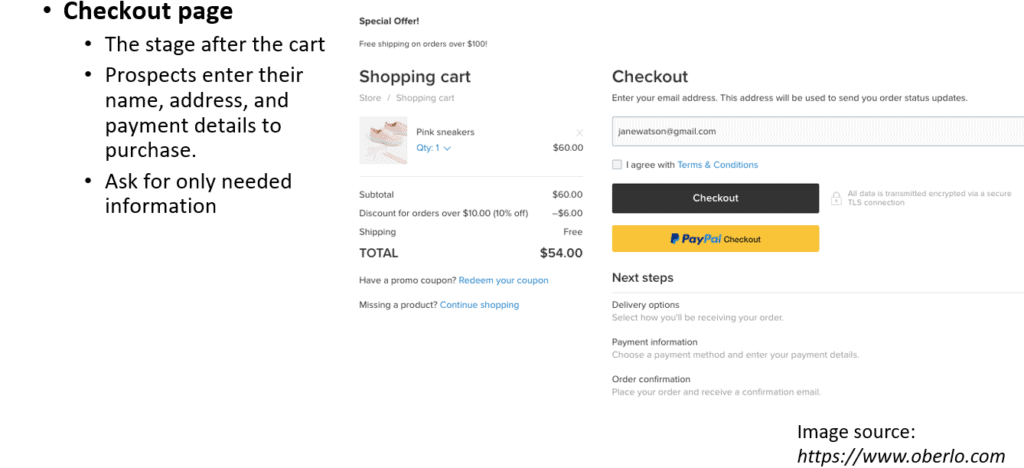
A product page provides specific details about individual products or services. This page includes a clear CTA such as “Purchase.” A checkout page usually appears after the cart. Prospects (or potential customers) enter their name, address, and payment details to complete a purchase. The page should ask only for the information needed so that prospects do not feel uncomfortable or inconvenienced.
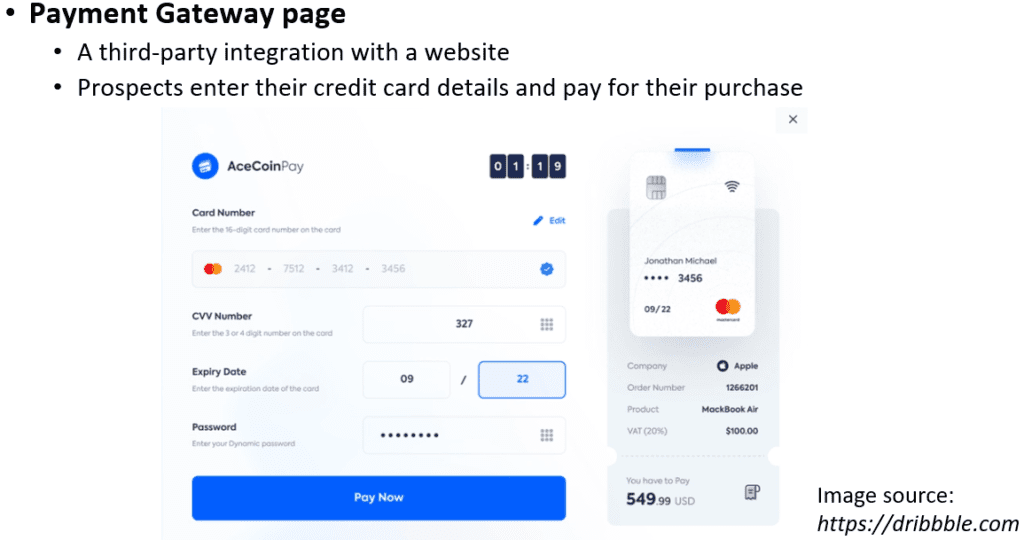
A payment gateway page does not belong to the website itself; instead, it is a third-party page integrated into the site. On this page, prospects enter their credit card details and pay for their purchase. A lead-generation page clearly explains why visitors should enter their contact details into a web form to access the lead magnet (such as an ebook, webinar, demo, or trial version).

Supporting pages of a website
In addition to main pages, a website has supporting pages such as a blog, news, FAQs, testimonials, privacy policy, terms and conditions, and a thank-you page. Supporting pages aim to build customers’ brand experience and brand affinity. First, a blog page provides customers with useful information to help them understand the brand and choose it as the solution to their needs. A news page keeps people up to date with developments in a company (or organization). Companies use this page to show visitors how dynamic they are.


A FAQs page provides answers to commonly asked questions about the business, products, or services. A testimonials page allows visitors to read third-party reviews from customers, which is a very powerful way to drive positive referrals.


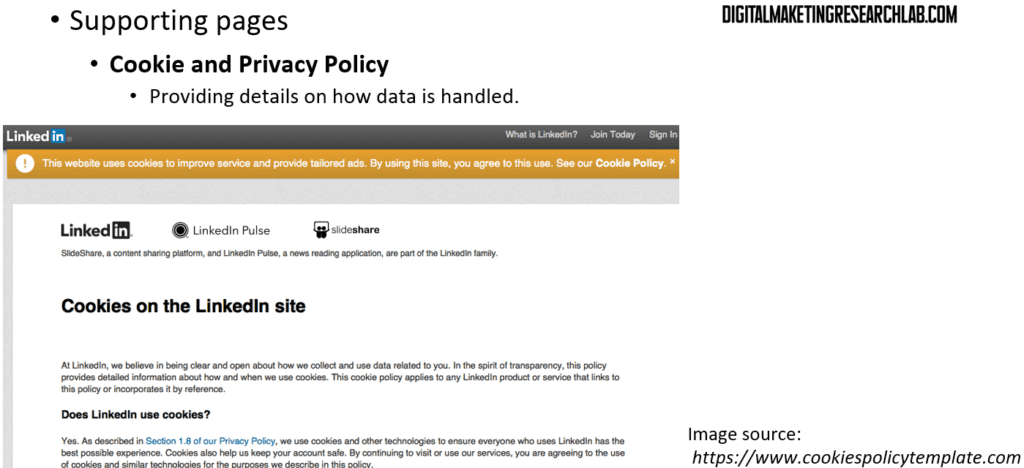
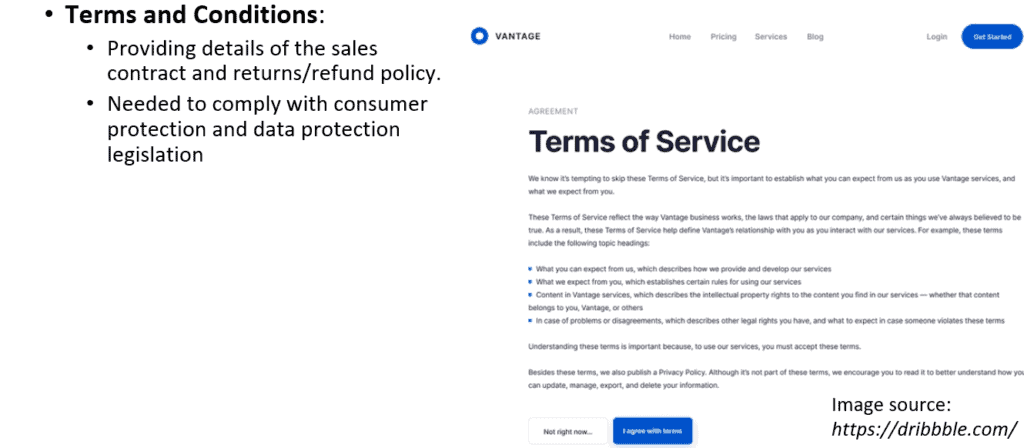
A cookie and privacy policy page provides details on how collected data is handled. A terms and conditions page provides details of the sales contract and the returns/refund policy. For eCommerce websites in particular, this information is required to comply with consumer protection and data protection legislation.
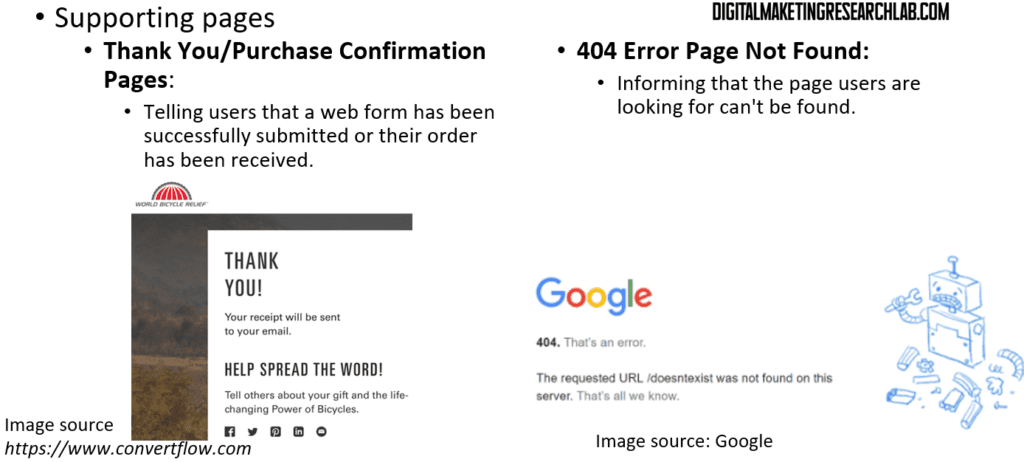
A thank-you/purchase confirmation page tells visitors that a web form has been successfully submitted or that their order has been received. A 404 error page (page not found) informs visitors that the page they are looking for cannot be found
*Reference
Hanlon, A. (2021). Digital marketing: strategic planning & integration. Sage.
Digital Marketing Institute (2021). Introduction to Digital Marketing.